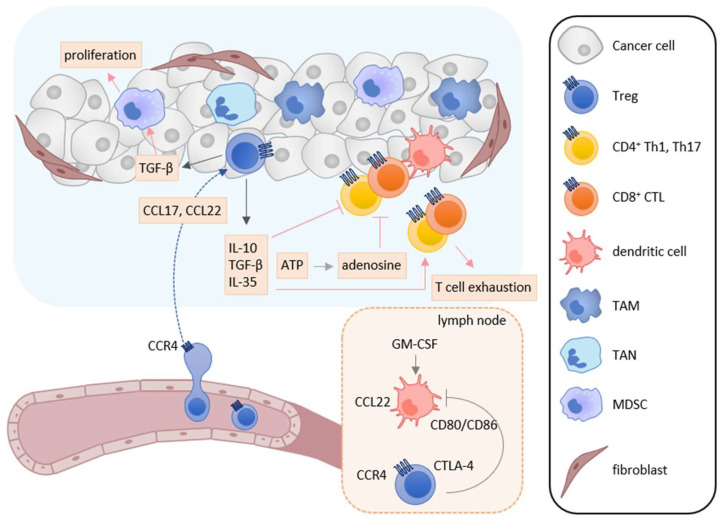
Figure 3.
Roles of Treg cells in tumor immunity. In the tumor microenvironment, TAMs, TANs, tumor cells, and cancer-associated fibroblasts secrete CCL17 and/or CCL22, and recruit CCR4-expressing Treg cells into tumor tissues. Infiltrated Treg cells secret immunosuppressive cytokines such as IL-10, TGF-β, and IL-35. These cytokines suppress the activation and induction of tumor-specific T cell responses and induce T cell exhaustion. TGF-β also enhances the differentiation and immunosuppressive function of MDSCs. Furthermore, adenosine is generated from ATP derived from apoptotic Treg cells and inhibits the function and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells also inhibit the costimulatory signals of DCs to induce tumor-specific T cell responses by the CTLA-4-CD80/CD86 interaction.