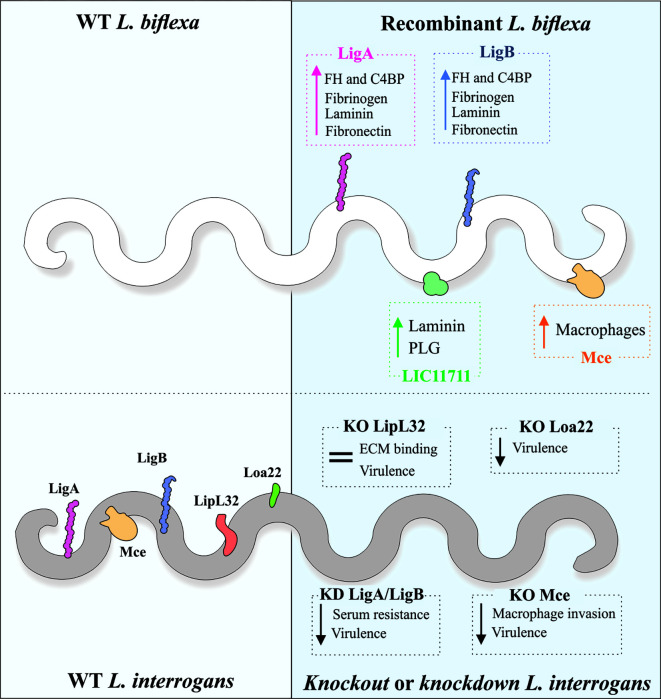
Figure 2.
Genetic tools and mutant evaluation of Leptospira. As the saprophytic L. biflexa lacks most of the virulence-associated proteins, it is used as a surrogate for the expression of pathogen-specific proteins and gain-of-function phenotype evaluation. Increased binding to ECM and plasma components has been observed in recombinant L. biflexa expressing L. interrogans proteins. Contrarily to this strategy, knockout (KO) or knockdown (KD) in the pathogenic L. interrogans has been used to evaluate loss-of-function phenotypes, in comparison to the wild-type strain. Reduced virulence in animal model was observed for KD double LigA/LigB, KO Loa22 and KO Mce mutants. KO of LipL32, the major lipoprotein of pathogenic leptospires, did not alter virulence or ECM binding.