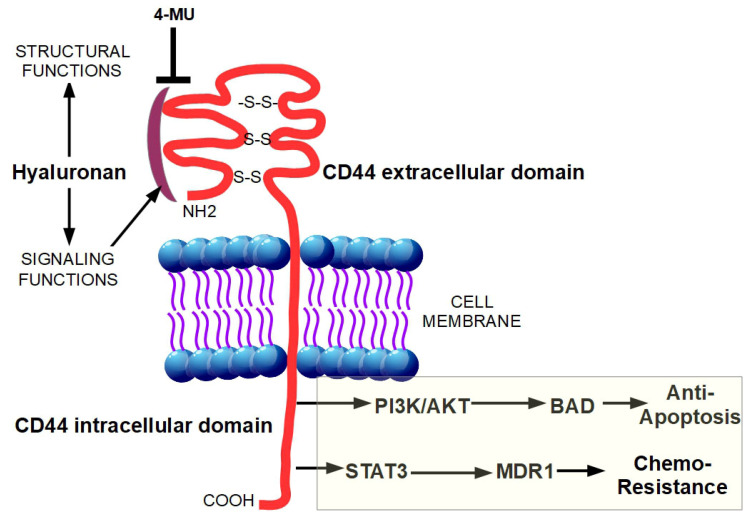
Figure 2.
Binding of hyaluronan to CD44 unleashes a pro-tumoral intracellular signaling. The intracellular signaling functions of hyaluronan are triggered after its binding with CD44. This interaction results in the increased expression of the multi-drug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) through STAT3 activation and in the activation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K/AkT) signaling pathway, causing phosphorylation of Bad, and the subsequent downregulation of apoptosis. The hyaluronan synthesis inhibitor, 4-methylumbelliferone (4-MU), inhibits cell migration, proliferation, and invasion by blocking the interaction between hyaluronan and CD44.