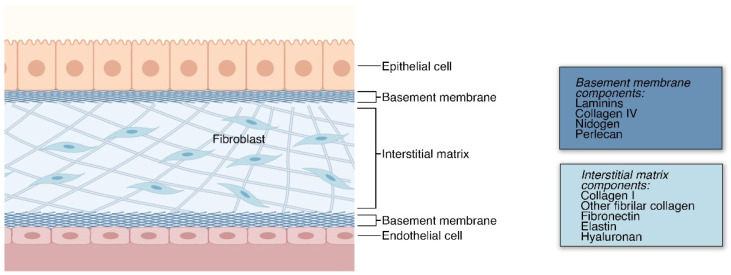
Figure 1.
Organ stratification by cell type and ECM type. In most organs, layering of cells and the ECM is observed. The outer most layer comprises of the epithelial cells which have specialized functions specific to the organs. These epithelial cells are anchored to the organ via a basement membrane which has a plethora of functions. Below this is the IM which houses the fibroblasts and fibrillar ECM proteins responsible for structural support. Bordering the IM is another layer of basement membrane which is associated with the blood vessel components, such as the endothelial cells. Both ECM types are comprised of a different set of ECM proteins. The IM, due to its functions in structure of the organs and tissues, is comprised of fibrillar ECM, such as fibronectin and collagen I. Whereas, the basement membrane is comprised of laminins and other proteins that are essential for epithelial and endothelial cell homeostasis.