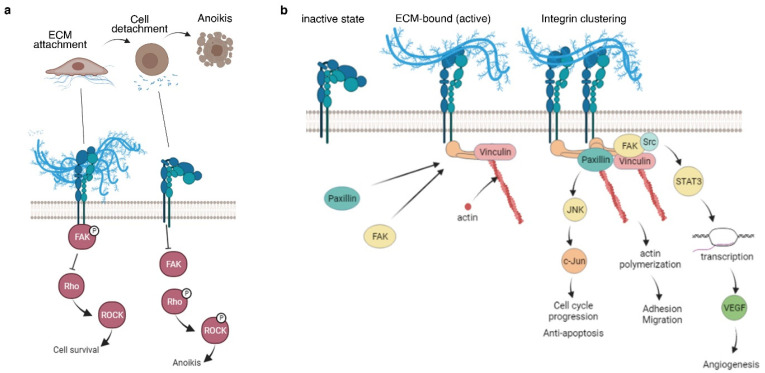
Figure 2.
ECM–integrin signaling. The most established transduction pathway for ECM interactions to the cell is through integrin signaling. (a) During cell detachment, activation of ROCK signaling leads to anoikis [74]. Thus, inhibition of ROCK has been beneficial in tissue engineering to prevent cell death during cell dissociation, especially in stem cells [75]. (b) Integrin signaling not only prevents cell death but also activates a plethora of signaling cascades in the cell [66,67,76,77]. Some of the downstream effects of integrin–ECM interactions include cell cycle progression leading to cell survival and proliferation, promotion of cell polarity, migration, adhesion, and transcriptional control of key pro-angiogenic factors (such as VEGF).