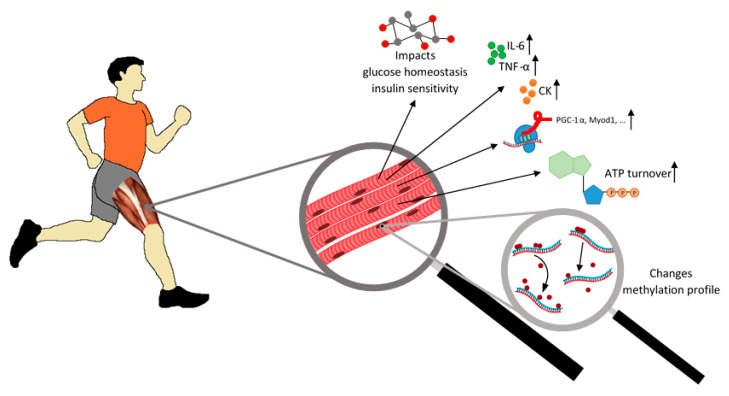
Figure 1.
Exercise affects the metabolism of muscle cells. Exercise impacts glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity, enhances the release of creatine kinase (CK), and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) as well as increases ATP turnover. Physical activity also induces changes in DNA methylation patterns and influences the expression of many genes in muscle tissue.