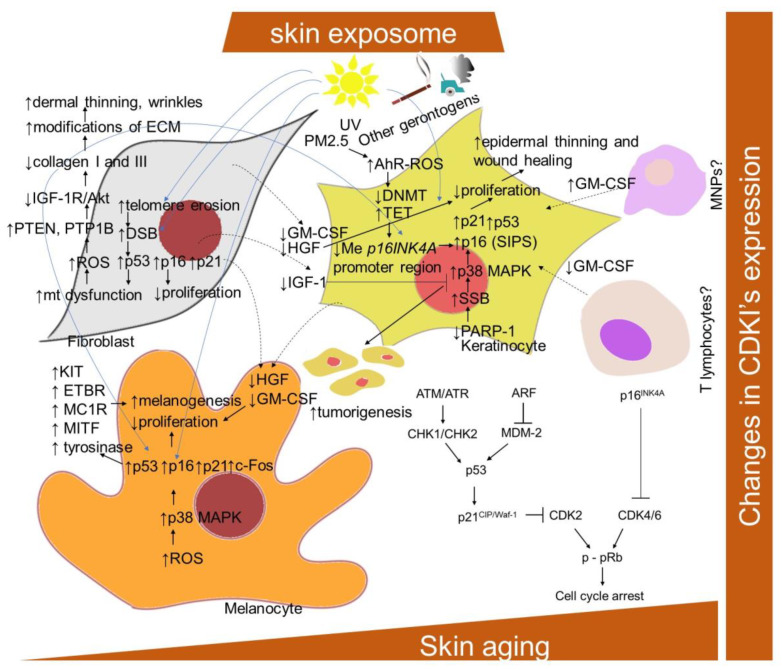
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of aging- and senescence-related changes associated with CDKIs expression. AhR-ROS, aryl hydrocarbon receptor and ROS-mediated pathway; Akt, protein kinase B; ATM, protein kinase ataxia-telangiectasia mutated; ATR, ATM and Rad3-related protein kinase; ARF, alternative reading frame protein; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; c-Fos, proto-oncogene; CDKI, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor; DSB, DNA double-strand break; DNMT, DNA methyltransferase; ECM, extracellular matrix; ETBR, endothelin–endothelin receptor B; GM-CSF, granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IGF-1R, insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; mt, mitochondria; KIT, transmembrane protein with tyrosine kinase activity; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MDM-2; mouse double minute 2 homolog; MITF, microphthalmia-associated transcription factor; MNPs, mononuclear phagocytes; NRAS and BRAF, proto-oncogenes; PARP-1, poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; p-pRb, phosphorylated retinoblastoma protein; PTP1B, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B; ROS, reactive oxygen species; PM2.5, particular matter 2.5; SSB, DNA single-strand break; TET, ten–eleven translocation enzyme.