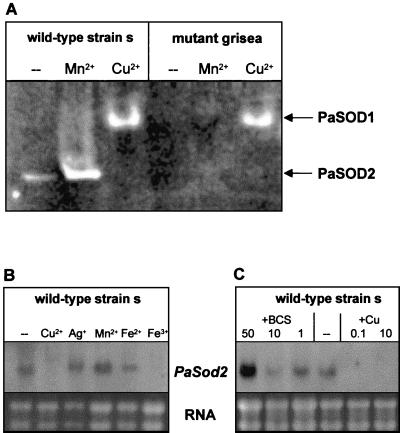
FIG. 7.
PaSOD2 is active in the wild-type strain and is dependent upon cellular copper. (A) SOD activity assay. Proteins were prepared from the wild-type strain and from mutant grisea after cultivation of these strains in CM without supplements (−) or in CM containing 100 μM MnCl2 (Mn2+) or 100 μM CuSO4 (Cu2+), run on a native polyacrylamide gel, and stained for SOD activity. (B) Northern blot analysis of PaSod2 transcription. Different metals (100 μM CuSO4 [Cu2+], 100 μM AgCl [Ag+], 100 μM MnCl2 [Mn2+], 100 μM FeSO4 [Fe2+], 100 μM FeCl3 [Fe3+]) were added to the medium. −, control. (C) Northern blot analysis of PaSod2 transcription at different copper concentrations. To reduce the copper concentration, cultures were grown in medium containing 1 μM BCS and 33 μM ascorbic acid or 10 μM BCS and 0.33 mM ascorbic acid or 50 μM BCS and 1.7 mM ascorbic acid. Copper levels were increased by the addition of 0.1 or 10 μM CuSO4 to the medium. −, no addition of CuSO4 (control).