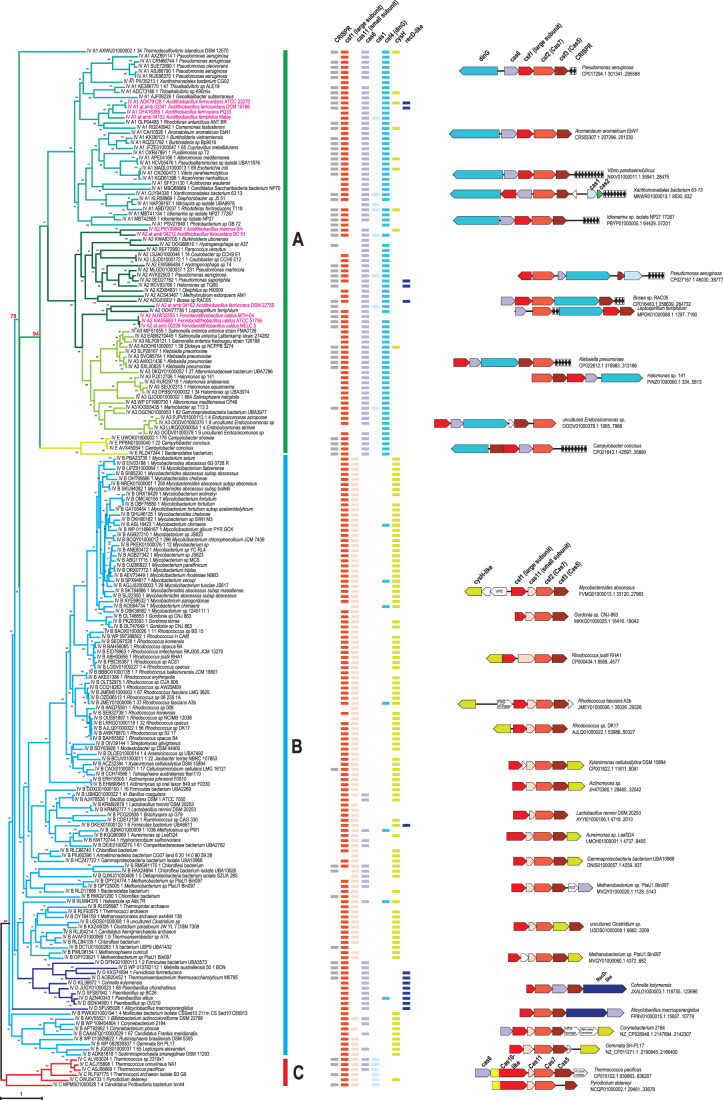
FIG. 1.
(A–C) Phylogenetic analysis of Cas7 (Csf2) and comparative genomic analysis of type IV systems. Phylogenetic tree for 204 representatives of Cas7 (Csf2) shown on the left was built using the IQ-TREE method as described in the Methods. The branches are colored according to the recently proposed classification of the type IV systems.6 Each leaf is denoted by subtype (IV-A1, IV-A2, IV-A3, IV-B, IV-C, IV-D, IV-E) as recently proposed,6 protein identifier, and species name. Supporting values were calculated by the IQ-TREE program. Several key values supporting monophyly of type IV-A and type IV-C are highlighted in red. The colored lines behind the tree show the amended proposal for classification of these systems based on this work as follows: green, type IV-A; blue, type IV-B; and red, type IV-C. The phyletic pattern (presence of a gene in the type IV locus in the respective genome) is shown by rectangles, which are color coded according to the legend above. Representative type IV core gene neighborhoods are shown behind the patterns and color coded according to the gene designation shown for each system once. The genes and CRISPR arrays are shown to scale, and accession for respective genomic partition, species name, and coordinates of the region are indicated on the right. A few genes that are inserted into type IV loci are shown by blank arrows, with short name (if any) indicated inside the arrow. VIP2, ADP phosphoribosyltransferase VIP2; FlhG, MinD-like ATPase involved in chromosome partitioning or flagellar assembly; HTH, helix-turn-helix, DNA binding; TGT, queuine tRNA-ribosyltransferase. Note: To visualize the details in this figure, a 200% zoom is recommended.