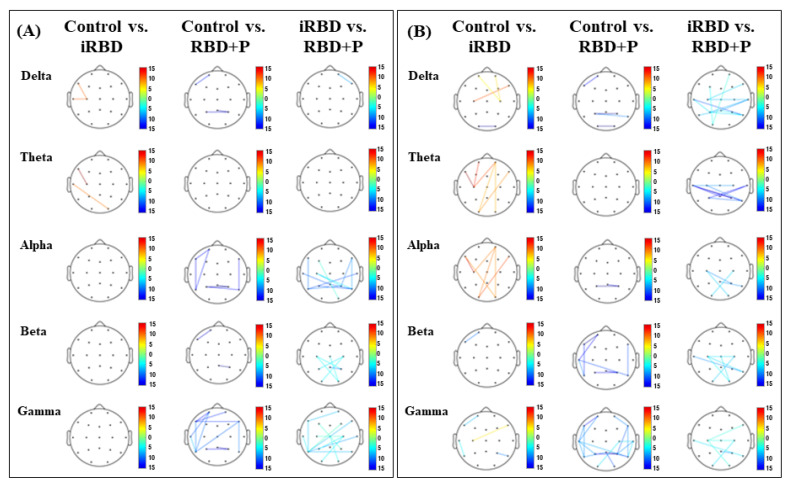
Figure 2.
The CCC between electrode pairs shown with statistical significance at p < 0.05 during NREM N2 (A) and REM sleep (B). (A) During NREM N2 sleep stage, the iRBD group revealed a lower alpha and gamma band CCC in frontal, temporal, and parietal areas compared with control group, whereas higher alpha band coherence in frontal, central, and temporal areas, higher beta band CCC in parietal and occipital areas, compared with RBD+P patients. In RBD+P patients, CCC in frontal, central, and temporal alpha power, and CCC in frontal, central, temporal gamma power during NREM2 sleep were lower than controls, and also CCC in frontal, central, and temporal alpha power, CCC in central, parietal, and occipital beta power, as well as CCC in frontal, central, temporal, and occipital gamma power were lower than the iRBD group. (B) During REM sleep, iRBD patients showed a considerably higher CCC in theta and alpha bands in frontal, central, and occipital areas compared with control subjects. The RBD+P group showed a lower CCC in beta band in frontal and temporal areas, and lower CCC in gamma band in frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital areas than the control group. In addition, the RBD+P patients had a lower delta, theta, alpha, beta, and gamma band CCC in central, temporal, parietal, and occipital areas compared with iRBD patients. Abbreviation: CCC, corticocortical coherence; NREM, non-rapid eye movement; REM, rapid eye movement; iRBD, idiopathic RBD; RBD+P, RBD with Parkinsonism.