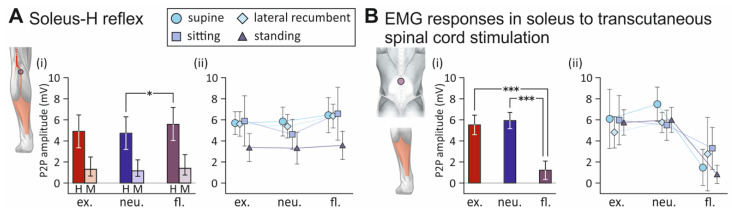
Figure 3.
Influence of the spine alignment condition on M waves and H reflexes as well as electromyographic (EMG) responses to transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation in soleus: group results. (A) (i) Marginal mean EMG peak-to-peak (P2P) amplitudes of H reflexes (H) and M waves (M) elicited across body positions with extended (ex.), neutral (neu.), and flexed (fl.) spine. P2P amplitudes of H reflexes were significantly larger with a flexed than with a neutral spine. (ii) P2P amplitudes of H reflexes elicited with different body positions and spine alignment conditions. (B) (i) Marginal mean P2P amplitudes of soleus responses to transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation across body positions elicited in different spine alignment conditions. P2P amplitudes were significantly smaller with flexed spine alignment compared to extended and neutral alignments. (ii) P2P amplitudes of EMG responses elicited with different body positions and spine alignment conditions. Whiskers extend from the lower to the upper limits of the respective 95% confidence intervals. Asterisks denote significant results of pairwise contrasts (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.0001).