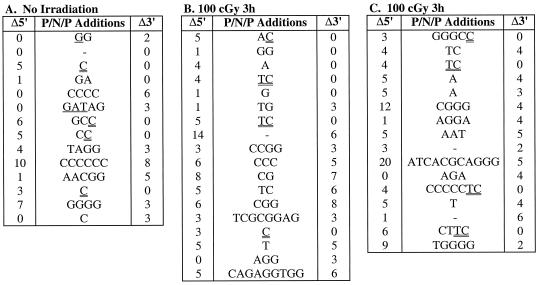
FIG. 1.
Effect of irradiation on coding end processing in wild-type thymic lymphoma cells. VL3-3M2 cells were transfected with pDR42, at various times before (B) or after (C) treatment with 0 (A) or 100 cGy of γ-irradiation, as indicated. After 48 h of culture, plasmid DNA was recovered and used to transform E. coli. pDR42 recombinant plasmids were purified from chloramphenicol-resistant colonies, and the coding junctions were sequenced. Shown are the 5′ P (single underline), N, and 3′ P (double underline) additions (P/N/P) at the CJ for each recombinant pDR42 clone. The number of nucleotides deleted from the 5′ (Δ5′) and 3′ (Δ3′) coding flanks are also indicated. P nucleotides were identified based on palindromy with the 3′ end of the 5′ coding flank (5′-ACAGGAAACAGGATC-3′) or the 5′ end of the 3′ coding flank (5′-GATGATATCGTCGAC-3′) sequences. For junctions where nucleotides could be assigned either to the coding flank or as P additions, the assignment was made to minimize the degree of P additions. The data represent independent clones derived from two independent transfections. The frequencies of independent recombinants sequenced were 93% (A), 100% (B), and 100% (C).