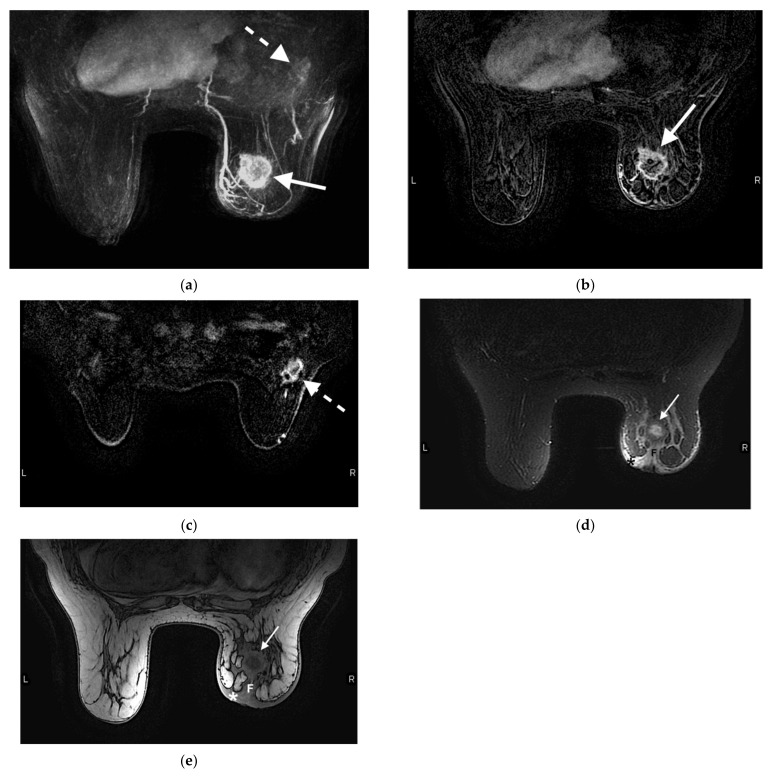
Figure 5.
Example protocol of an abMRI. 61-year-old woman presented for screening MRI. (a) Maximum intensity projection image illustrates a 3.8 × 3.2 × 4.6 cm rim enhancing centrally necrotic mass in the right breast (arrow). Biopsy of this lesion yielded invasive ductal carcinoma. The enhancing axillary lymph nodes (dashed arrow) are asymmetric compared to the contralateral side, and was biopsy-proven metastatic disease. The right breast is asymmetrically decreased in size. (b) Contrast-enhanced axial T1-weighted fat-suppressed image demonstrates the same rim-enhancing mass in the right breast (arrow). (c) Contrast-enhanced axial T1-weighted fat-suppressed image demonstrates an irregular 2.8 × 2.0 cm spiculated mass, compatible with metastatic lymph nodes (dashed arrow). (d) Contrast-enhanced axial T2-weighted fat-suppressed image demonstrates the same right breast mass (arrow) with associated skin thickening (*), compatible with skin involvement. Associated fibrosis (F) results in nipple retraction, indicating nipple involvement. (e) Non-contrast-enhanced T1-weighted axial image without fat suppression redemonstrates the mass (arrow), skin thickening (*) and fibrosis (F) resulting in nipple retraction. In addition to the above sequences, a full protocol MRI would also include a T1-weighted axial noncontrast image with fat suppression, at least three other dynamic axial T1-weighted post-contrast sequences, and a sagittal delayed post-contrast sequence.