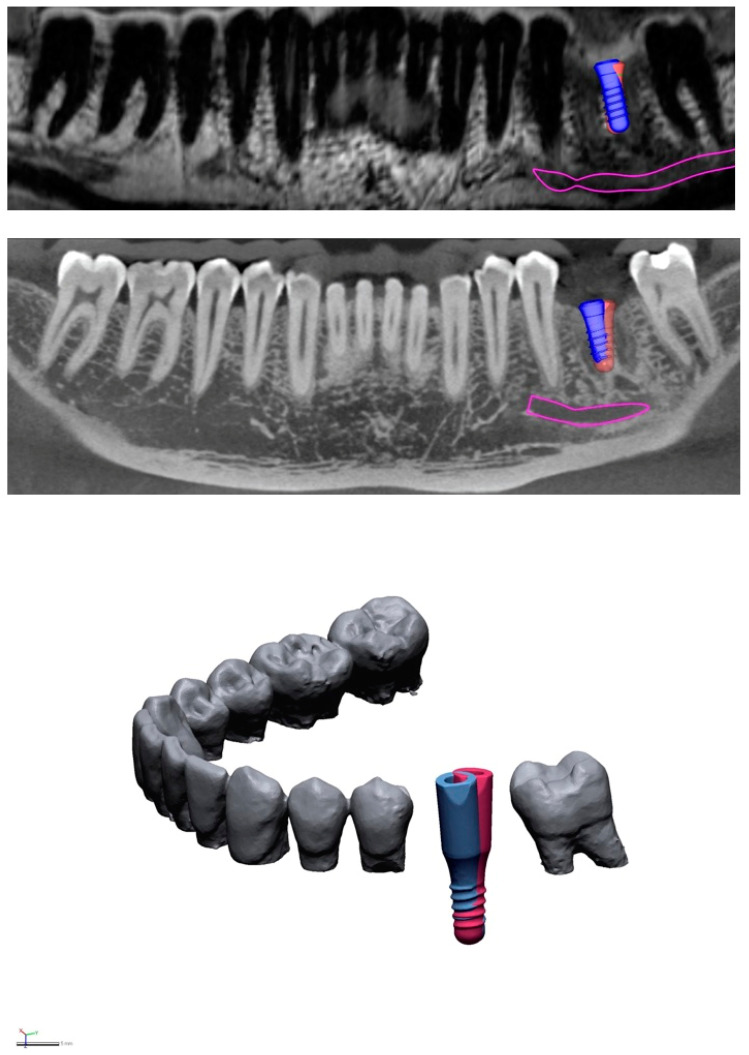
Figure 1.
Illustrative slices from MRI (top) and CBCT (middle) scans. Virtual implant placement was performed twice in each imaging modality with a time lag in between to prevent learning bias. The slices show superimposition of the two plans in area 36 (blue implant: first implant plan, red implant: second implant plan). Deviations can be seen between the two plans regarding implant tip, entry-level, and axis. Pink: nerve canal (CBCT) and alveolar bundle (MRI). Comparison of the two images reveals that image quality is superior in CBCT, due to its higher resolution and lower susceptibility to motion artifacts. (Bottom): The virtual plans of both modalities were exported from the 3D planning software and imported into reverse-engineering software. Using this software, geometric deviations were evaluated at the implant tip, entry-level, and axis.