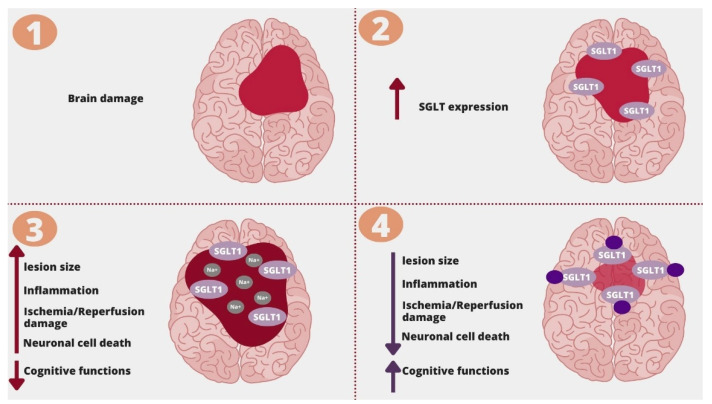
Figure 4.
SGLT1 inhibition and ischemic brain damage. 1. Brain damage; 2. In the area of brain damage, there is an increase in the expression of SGLT1; 3. Sodium influx through SGLT1 receptors is associated with increased ischemia/reperfusion damage, lesion size, edema, inflammation, neuronal cell death, and decline in cognitive functions; 4. SGLT receptor blockage/knockdown was associated with improvement in damages caused by ischemia and ischemia/reperfusion damage.