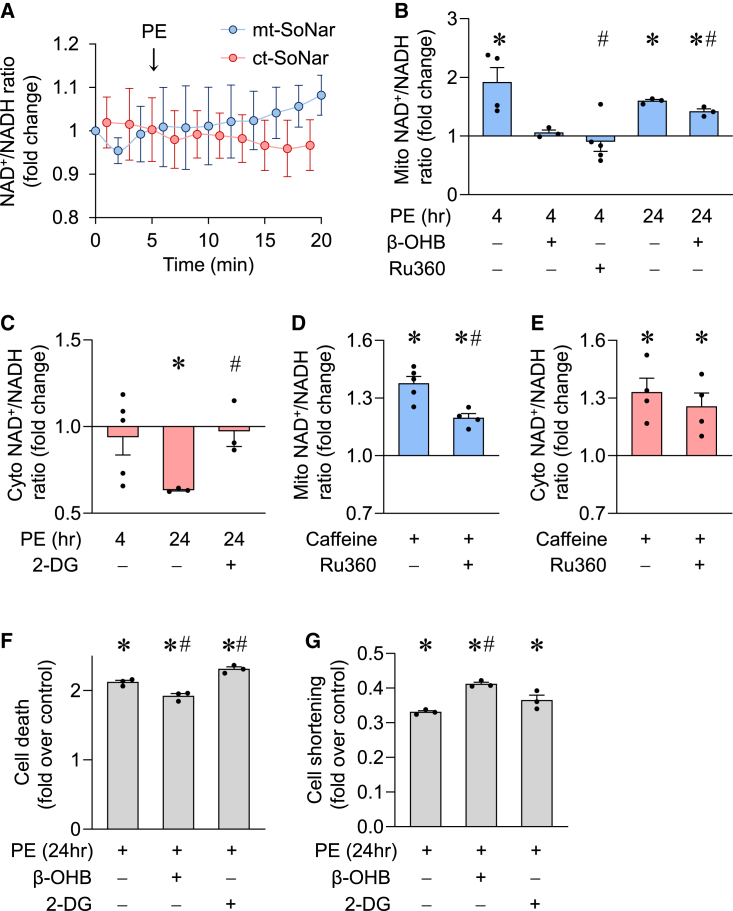
Figure 4.
Subcellular NAD+/NADH ratios and pathological stress
(A) Summarized data showing time-dependent changes of cytosolic or mitochondrial NAD+/NADH ratio in adult cardiomyocytes during acute phenylephrine (PE, 10 μM) treatment. n = 3–4.
(B and C) Mitochondrial or cytosolic NAD+/NADH ratio measured by mt-SoNar or ct-SoNar, respectively, before and after 4 or 24 h PE (10 μM) incubation with or without 1 mM β-OHB, 10 μM Ru360, or 2 mM 2-DG. n = 3–5 rats. ∗p < 0.05 versus control (value is set as 1.0); #p < 0.05 versus PE.
(D and E) Mitochondrial (D) or cytosolic (E) NAD+/NADH ratio in response to acute addition of 10 mM caffeine, which significantly increases cytosolic Ca2+, and the effects of 10 μM Ru360. n = 4–5 rats. ∗p < 0.05 versus control (value is set as 1.0); #p < 0.05 versus caffeine.
(F and G) Effects of PE (10 μM for 24 h) on cell death (F) and contraction amplitude (G) of adult cardiomyocytes. n = 3 rats. ∗p < 0.05 versus control (value is set as 1.0); #p < 0.05 versus PE.
Data are presented as mean ± SEM. See also Figure S2.