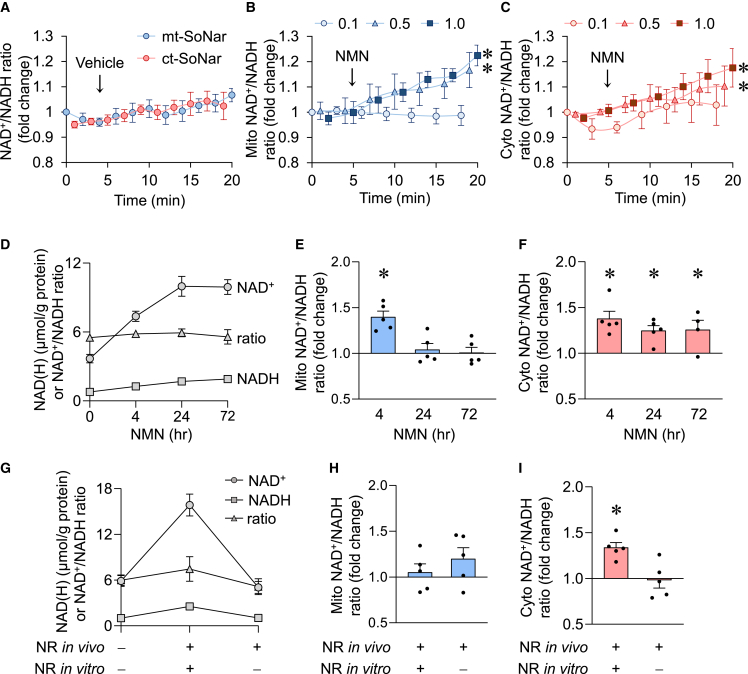
Figure 5.
Mitochondrial NAD+/NADH redox is maintained despite significantly enlarged NAD pool
(A–C) Time-dependent responses of mitochondrial (mito, blue) or cytosolic (cyto, red) NAD+/NADH ratio to vehicle (A) or different doses of NAD+ precursor NMN (B and C). n = 3–5 rats. ∗p < 0.05 versus 0.1 mM NMN by two-way ANOVA.
(D–F) Total intracellular NAD+ level, NADH level, and NAD+/NADH ratio (D), and mitochondrial (E) or cytosolic (F) NAD+/NADH ratio after NMN (1 mM) incubation for 0, 4, 24, or 72 h. n = 4–8 rats. ∗p < 0.05 versus control (0 h, value is set as 1.0).
(G–I) Total intracellular NAD+ level, NADH level, and NAD+/NADH ratio (G), and mitochondrial (H) or cytosolic (I) NAD+/NADH ratio after long-term treatment of NAD+ precursor NR in vivo (500 mg/kg/day intraperitoneally for 10 days in rats) followed by NR or vehicle in cell culture (1 mM NR for 3 days on cardiomyocytes isolated from the rats after 10 days of in vivo NR treatment). n = 5–9 rats. ∗p < 0.05 versus no NR (value is set as 1.0).
Data are presented as mean ± SEM. See also Figure S3.