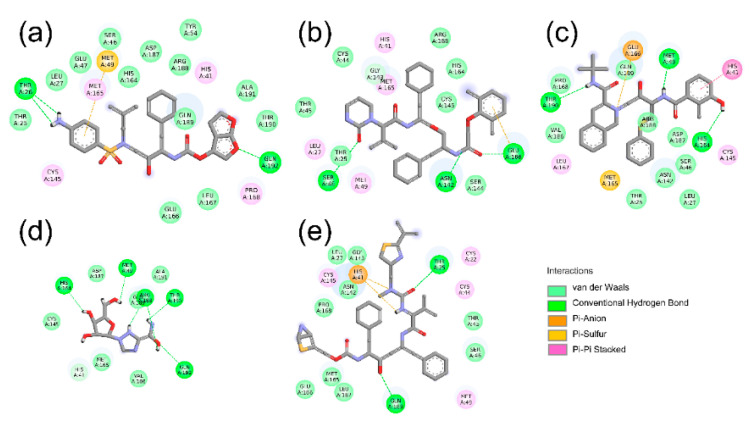
Figure 6.
The interactions of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro-DRV/LPV/NFV/RBV/RTV complexes displayed as 2D image. In SARS-CoV-2 Mpro-DRV complex (a), Met49 with DRV forms a Pi–sulfur interaction and Thr26 with DRV forms two hydrogen bonds; in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro-LPV complex (b), the side chain of Glu366 with LPV forms a Pi–anion interaction, and Asn142, Ser46, and Glu166 are involved in three hydrogen bond interactions; in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro-NFV complex (c), the catalytic site His41 with NFV has a stable Pi–Pi stacked; in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro-RBV complex (d), two Van der Waals forces were produced in Gln189 and Thr190 with RBV, and four Hydrogen bonds were formed between His164, Gln192, Met49, Arg188, and RBV; in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro-RTV complex (e), we can see two Pi–anion interactions and hydrogen bonds. DRV/LPV/NFV/RBV/RTV are shown as the stick models. C, O, and N atoms are colored by gray, red, and blue, respectively. Hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions that help to lock the inhibitor are shown in green and orange dashed lines, respectively.