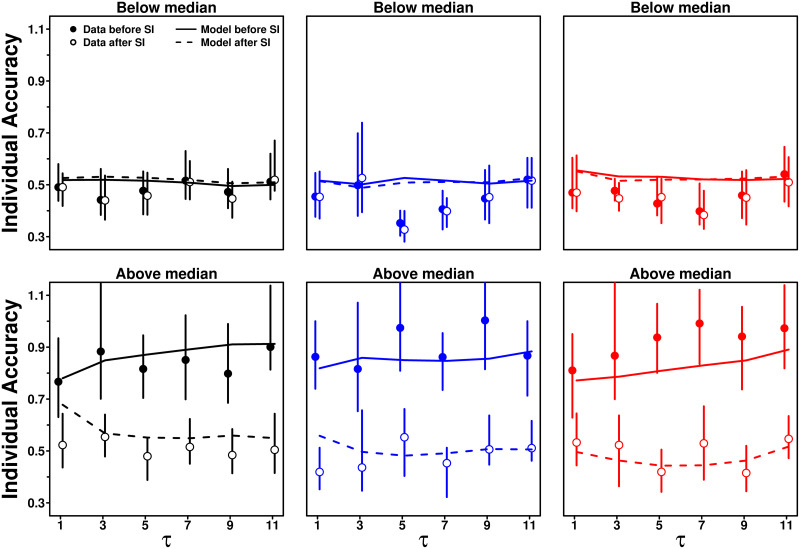
Fig 14. Individual accuracy against the number of shared estimates τ, before (filled dots) and after (empty circles) social information sharing, in the Random (black), Median (blue), and Shifted-Median (red) treatments.
In each condition, the subjects’ answers were separated according to their corresponding value of S with respect to the median of S. Solid and dashed lines are model simulations before and after social information sharing, respectively. When S is lower than the median, the subjects tend to keep their initial estimate, and individual accuracy therefore does not change much. When S is higher than the median, the subjects tend to compromise more with the social information, resulting in high improvements.