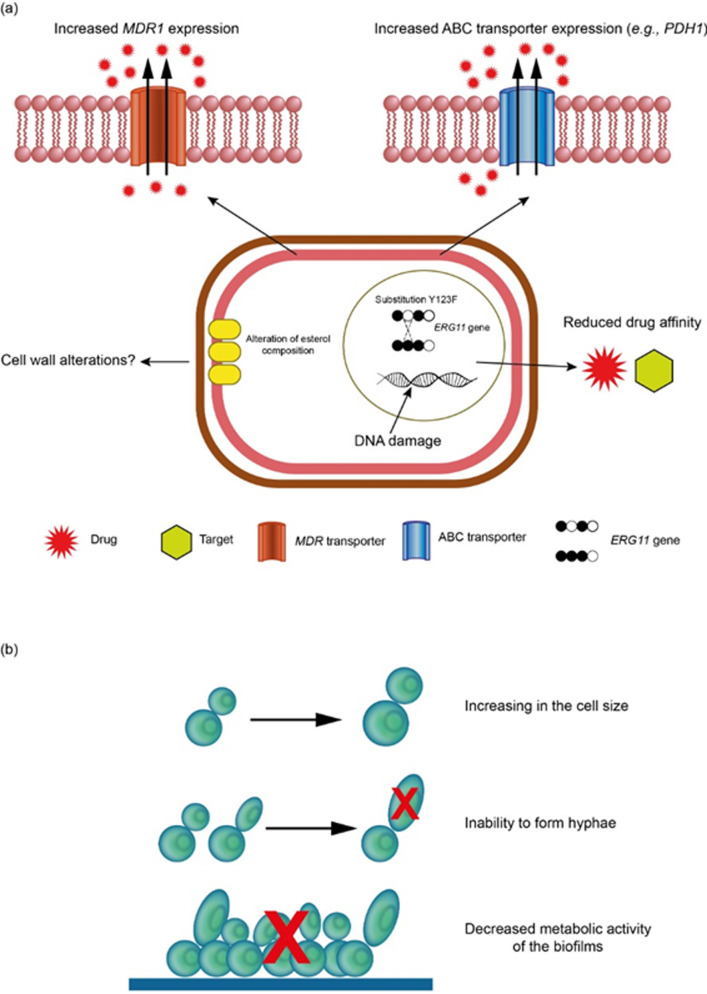
Fig 2. Cellular alterations induced by fungicides exposure in Candida spp.
(a) Mechanisms of resistance induced by fungicides in Candida spp. Azole resistance triggered by fungicide exposure shows up-regulation of ABC multidrug transporters, such as PDH1. In addition, amino acid substitution Y132F in the erg11 gene can occur, suggesting that this selected resistance is mainly associated with increased drug efflux through ATP-dependent pumps. Sterol composition and DNA damage are also consequences of fungicide exposure. (b) Alterations in morphophysiology and virulence of Candida spp. caused by fungicides. Candida spp. exposure to fungicides showed an expanded cell size, inability to form hyphae, and significantly altered time of adhesion and decreased the metabolic activity of biofilms. ABC, ATP-binding cassette.