Figure 2.
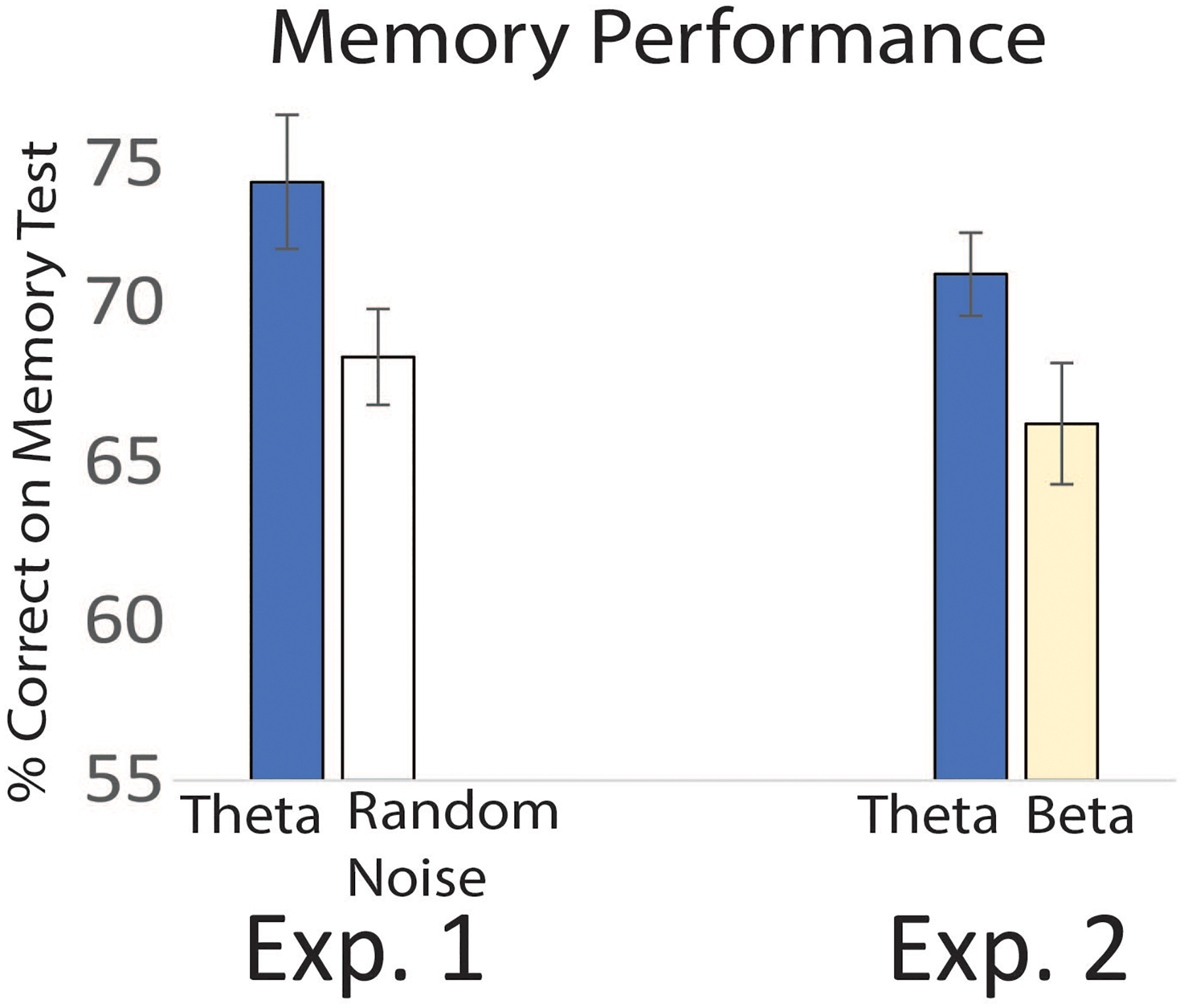
In the first experiment, the group that received theta brain entrainment scored better on the memory test compared to the group that received white noise. In the second experiment, the group that received theta entrainment showed better memory results than the group that received beta entrainment. The difference between entrainment conditions was statistically significant, which means that these differences had a <5% probability of being due to random chance. The lines on the top of each bar represent the standard error of the mean, and they show how much the data points vary from the average.
