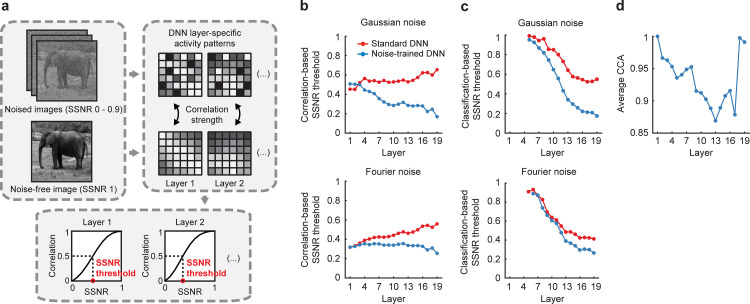
Fig 6. Layer-specific network changes caused by noise training.
(a) Depiction of method used for layer-specific noise susceptibility analysis. (b) Correlation-based SSNR thresholds for pretrained (red) and noise-trained (blue) versions of VGG-19 plotted by layer for objects shown in pixelated Gaussian noise or Fourier phase-scrambled noise. Layers 1 to 16, convolutional layers after rectification; layers 17 and 18, fully connected layers after rectification; layer 19, softmax output layer. Higher SSNR thresholds indicate greater susceptibility to noise. (c) Classification-based SSNR thresholds plotted by layer for pretrained and noise-trained networks. Multiclass SVMs were used to predict object category from layer-specific activity patterns. (d) Similarity of feature representations for pretrained and noise-trained versions of VGG-19, calculated using CCA. Data are available at https://osf.io/bxr2v/. CCA, canonical correlation analysis; DNN, deep neural network; SSNR, signal-to-signal-plus-noise ratio; SVM, support vector machine.