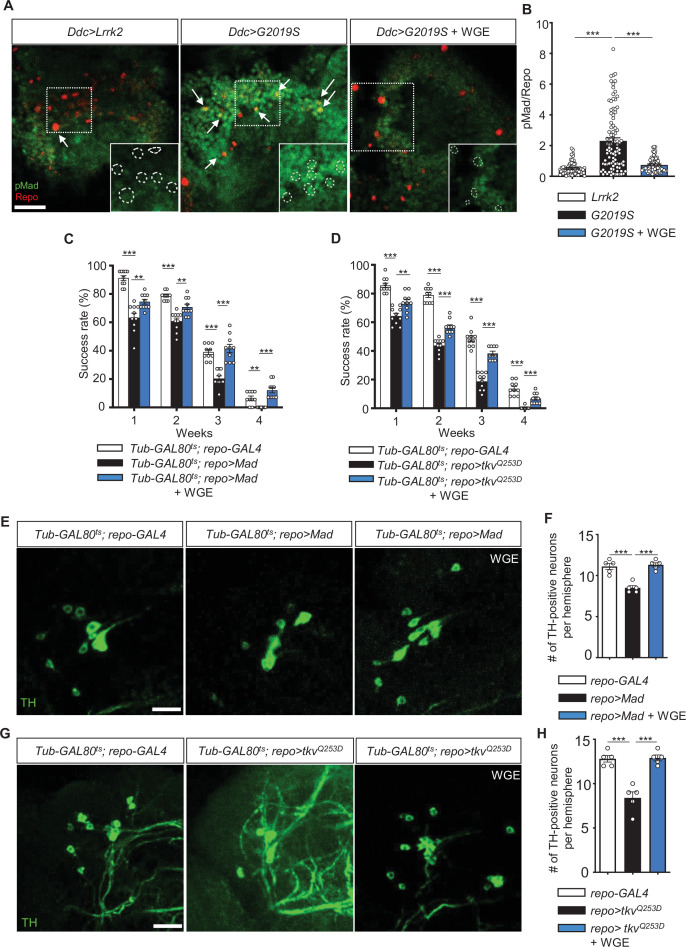
Figure 7. Water extract of Gastrodia elata Blume (WGE) downregulates G2019S-induced BMP/Mad signaling.
(A) Representative images of glial pMad staining in the adult PPL1 clusters of Ddc>Lrrk2, Ddc>G2019S, and WGE-fed Ddc>G2019S flies. White arrows indicate pMad signals co-localized with Repo, with single channels for pMad signals shown as insets. Bar: 10 μm. (B) Quantification (mean ± SEM, n > 60 for each genotype) of pMad signals normalized to Repo levels in glia of the indicated genotypes. One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc multiple comparison test (relative to Ddc>G2019S): ***p<0.001. (C, D) Climbing success rates (mean ± SEM, N = 10) at weeks 1–4 demonstrating that WGE treatment rescues locomotion deficits induced by glial overexpression of Mad (C) or tkvQ253D (D) in Tub-GAL80ts; repo-GAL4 flies. One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc multiple comparison test (relative to repo>Mad or repo>tkvQQ253D): **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (E, G) Representative images of 4-week-old adult brain showing TH staining of the PPL1 clusters of Tub-GAL80ts; repo-GAL4, Tub-GAL80ts; repo>Mad, and WGE-fed Tub-GAL80ts; repo>Mad flies (E), and Tub-GAL80ts; repo-GAL4, Tub-GAL80ts; repo>tkvQQ253D, and WGE-fed Tub-GAL80ts; repo>tkvQQ253D flies (G). Bars: 12.5 μm. (F, H) Bar graphs show mean ± SEM (N = 5) of TH-positive dopaminergic neurons in the PPL1 clusters of 4-week-old flies. One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc multiple comparison test (relative to Tub-GAL80ts; repo>Mad [F] or Tub-GAL80ts; repo>tkvQQ253D [H]): ***p<0.001.
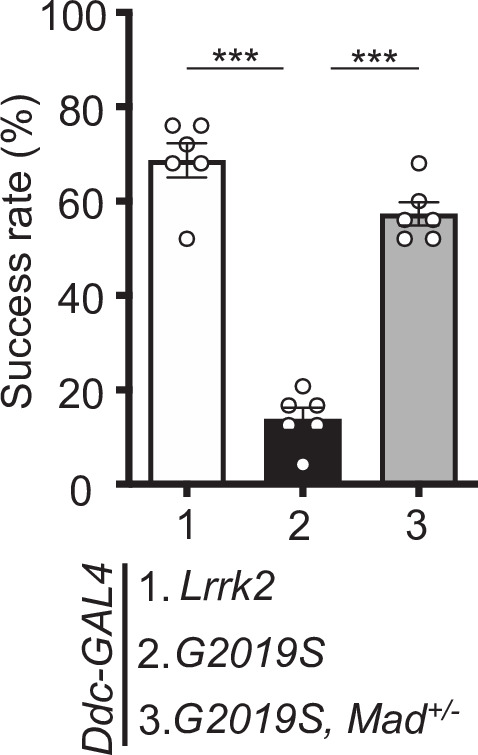
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Mad heterozygosity rescues the impaired locomotion of Ddc>G2019S flies.