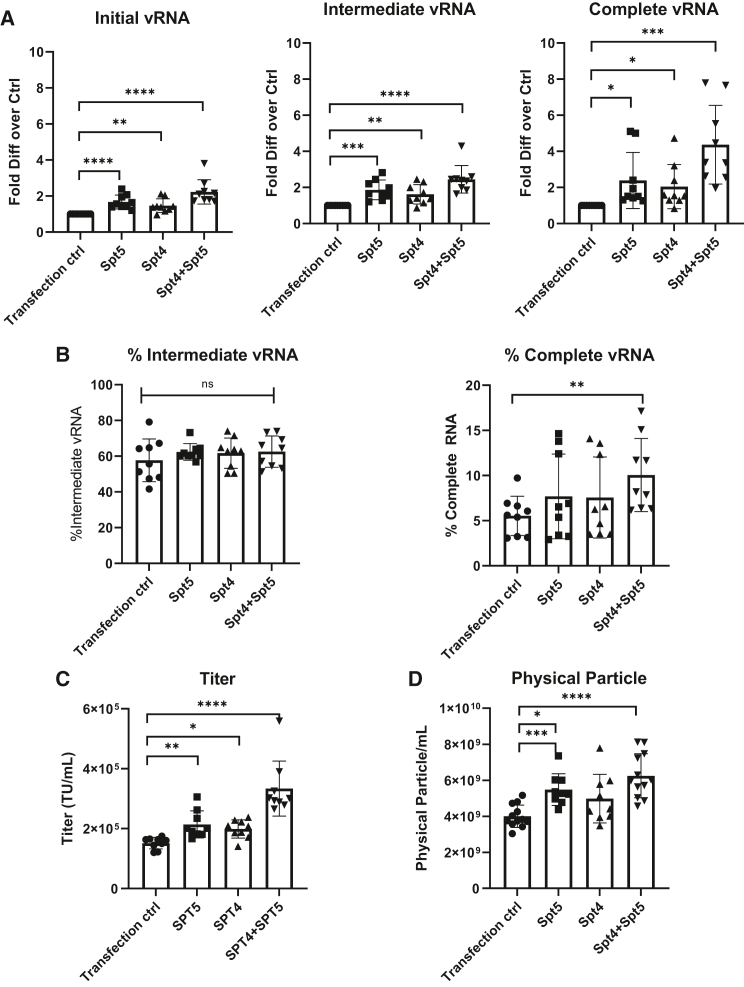
Figure 4.
Packaging with transcription elongation factors SPT4/5 increased vRNA completeness and vector titer
(A) The fold difference of initial, intermediate, and complete vRNA compared with the transfection control and (B) a percentage of intermediate and complete vRNA in parental HEK293T cells with SPT4/5 plasmids or a filler plasmid (n = 9 dishes identical cultures from three independent experiments; bars represent mean with SD; unpaired t test, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). The percentage of intermediate vRNA was calculated as the copies of intermediate vRNA divided by the copies of initial RNA. The percentage of complete vRNA was calculated as the copies of complete vRNA divided by the copies of initial vRNA. (C) Titers of Lenti/βAS3-FB packaged in parental HEK293T cells with SPT4/5 plasmids or a filler plasmid as the transfection control (an unpackageable GFP plasmid without lentiviral sequences) (n = 9 dishes identical cultures from three independent experiments; bars represent mean with SD; unpaired t test, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). (D) Concentration of physical particles measured by p24 ELISA (n = 9–12 dishes with identical cultures from three to four independent experiments; bars represent mean with SD; unpaired t test, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).