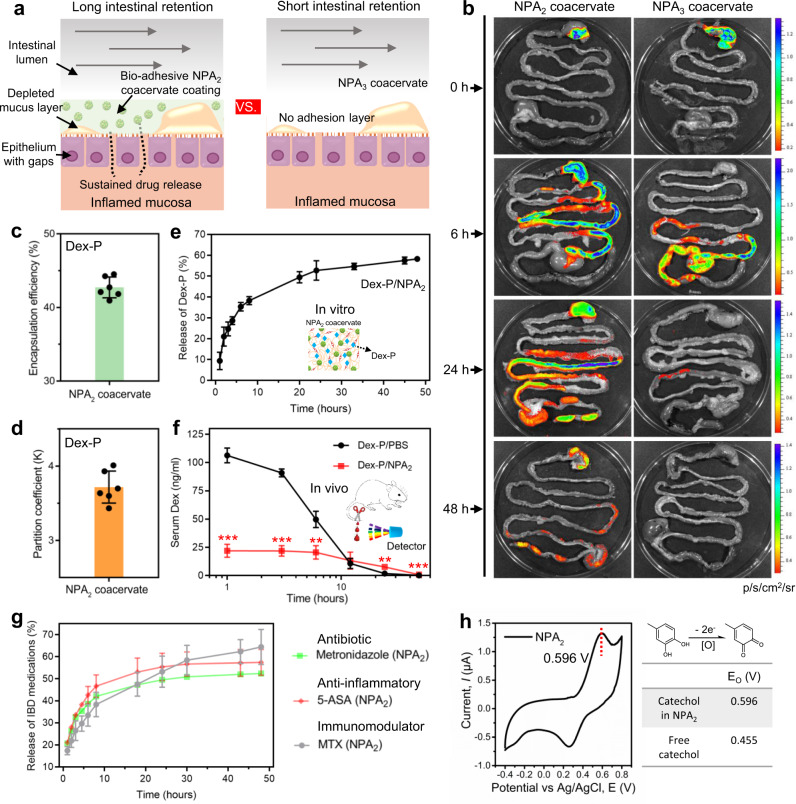
Fig. 3. NPA2 coacervate demonstrates prolonged retention and mediates sustained drug release in the GI tract.
a, b The bioadhesive NPA2 coacervate delivered via oral gavage adhered to the GI tract of SD rats for at least 2 days, whereas the control nonadhesive NPA3 coacervate showed short retention in the GI tract. c, d NPA2 coacervate has a high Dex-P encapsulation efficiency because of the hydrophobic component of its structure. n = 6 independent encapsulation tests. e NPA2 coacervate mediated sustained release of preloaded Dex-P over several days in vitro. f Dex-P-laden NPA2 coacervate delivered by oral gavage better sustained the serum Dex concentration at the lower therapeutic level compared with that of the oral gavage of Dex-P aqueous solution (Dex-P/PBS) in vivo. n = 3 biologically independent rats per group. g, h The condensed hydrophobic environment of NPA2 coacervate as revealed by an increased catechol oxidation potential (E0) of 0.596 V, facilitated the sustained release of a wide array of water-soluble small-molecular drugs including antibiotic metronidazole, anti-inflammatory 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), and immunoregulatory methotrexate disodium salt (MTX). Data were presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (two-tailed Student’s t-test). Source data are provided as a Source Data file for Fig. 3c–h.