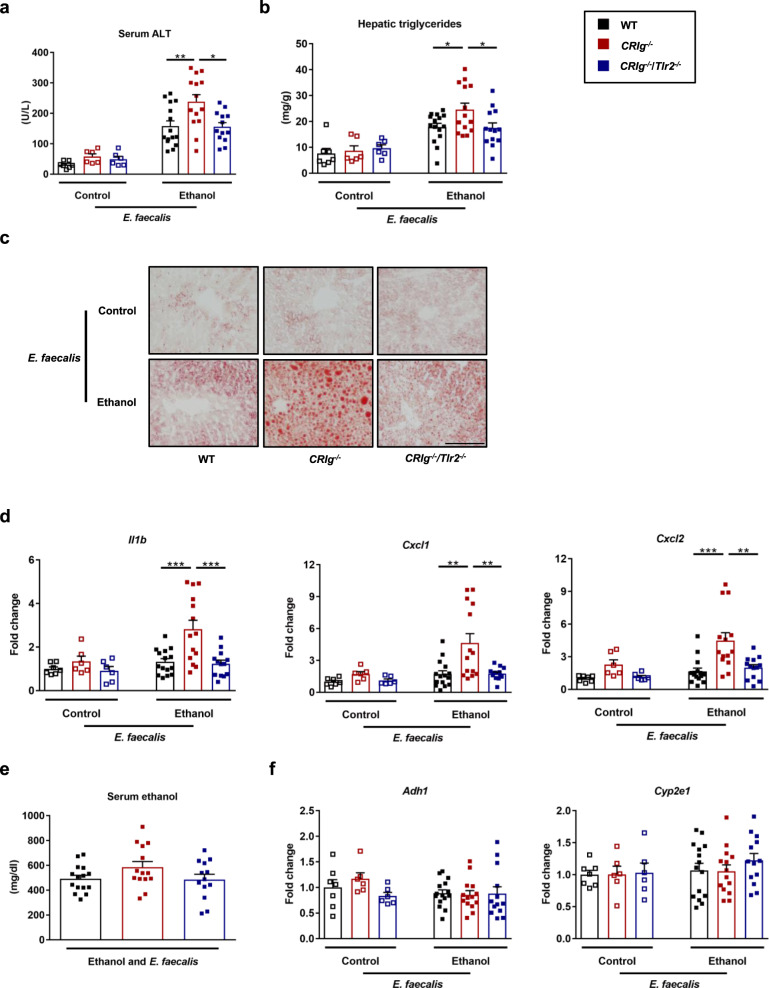
Fig. 3. CRIg−/− mice are more susceptible to E. faecalis- and ethanol-induced liver disease.
WT, CRIg−/− and CRIg−/−/Tlr2−/− mice were placed on the chronic–binge ethanol diet and gavaged with a cytolytic E. faecalis strain (5 × 108 colony forming units (CFUs)) every third day. a Serum levels of ALT. b Hepatic triglyceride content. c Representative oil red O-stained liver sections. d Hepatic levels of mRNAs encoding inflammatory cytokines and chemokines IL1B, CXCL1, and CXCL2. e Serum levels of ethanol in ethanol-fed mice. f Hepatic levels of Adh1 and Cyp2e1 mRNAs. Scale bar = 100 μm. Results are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. (a, b, d–f). P values among groups of mice fed with control diet or ethanol diet are determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey´s post-hoc test (a, b, d–f). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.