Fig. 6. Models of extracellular HH signalling antagonism by HHIP.
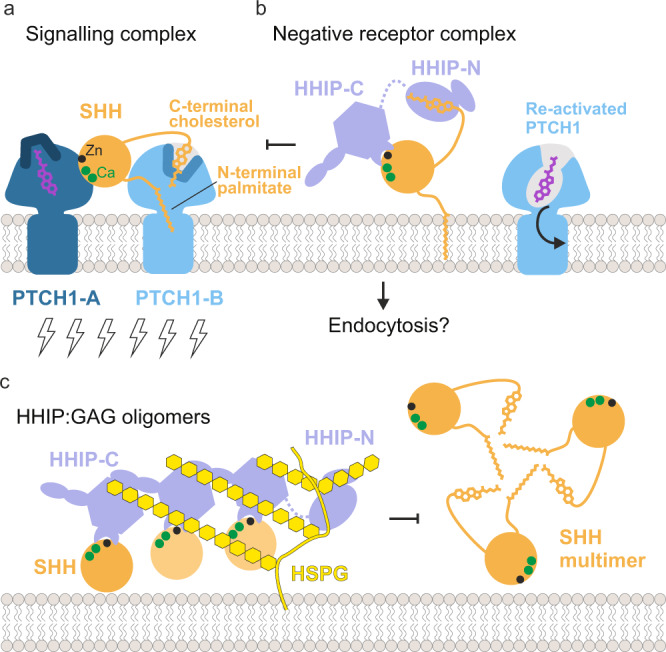
a A 2:1 interaction of PTCH1:pShhNc represents the active signalling complex. The pShhNc lipid appendages insert to seal channels in PTCH1-B. b HHIP-C targets the conserved high-affinity metal ion-binding site on the pShhNc surface (‘protein-protein interaction’), competing with binding from PTCH1-A and other co-receptors, whilst HHIP-N is able to contribute to this by targeting the C-terminal cholesterol moiety, possibly re-establishing PTCH1 cholesterol transport ability. It is also of note that HH signalling is activated via SMO CRD-cholesterol interaction, and competition of this by the HHIP-N CRD represents a possible additional mode of inhibition. Additionally, HHIP-mediated receptor endocytosis may act to remove SHH from the cell surface. c Cell surface GAG-mediated clustering represents a second modality for HH regulation by HHIP. The avidity of HHIP is increased by cluster formation at the proteoglycan layer, similar to how SHH lipoprotein multimers act to increase local morphogen concentration. The GAG-binding site in HHIP-N is also important for this process.
