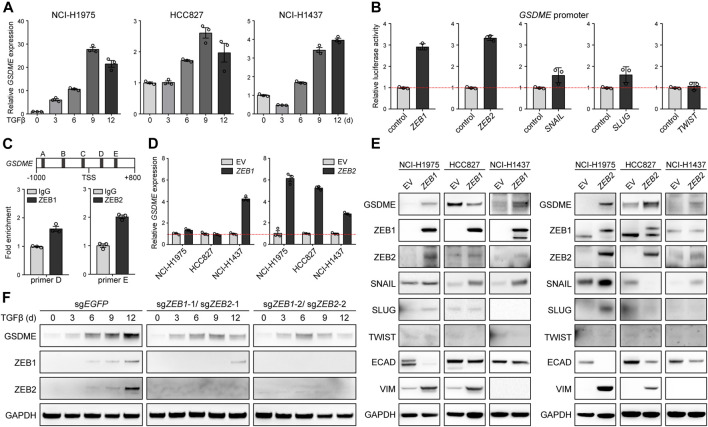
FIGURE 3.
Direct induction of GSDME transcription by the EMT activator ZEB1/2. (A) Three indicated lung cancer cell lines were treated with TGFβ (5 ng/μl) at a time course manner and analyzed by qPCR for GSDME gene expression. Data are means ± SEM pooled from three independent experiments. (B) Five core EMT-TFs (ZEB1, ZEB2, SNAIL, SLUG, and TWIST) were co-transfected with GSDME promoter fused with dual luciferase reporter system and luciferase activity was assayed against the vector control. Data are means ± SEM pooled from three independent experiments. (C) ZEB1 or ZEB2 was overexpressed in NCI-H1975 cells and ChIP-qPCR analysis was performed with primer sets flanking five predicted ZEB1/2-binding consensus sequence proximal to the GSDME TSS (transcription start site). ZEB1 and ZEB2 was observed to bind to (D,E) locus at the GSDME promoter region, respectively. Data are means ± SEM pooled from three independent experiments. (D) EMT-TFs ZEB1 or ZEB2 was overexpressed in three indicated lung cancer cell lines and analyzed by qPCR for GSDME gene expression. Data are means ± SEM pooled from three independent experiments. (E) EMT-TFs ZEB1 or ZEB2 was overexpressed in three indicated lung cancer cell lines and analyzed by Western blot for GSDME protein expression. EV, empty vector. (F) ZEB1 and ZEB2 were simultaneously knocked out in HCC827 cells using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Cells were treated with TGFβ (5 ng/μl) at a time course manner and analyzed by Western blot for GSDME protein expression.