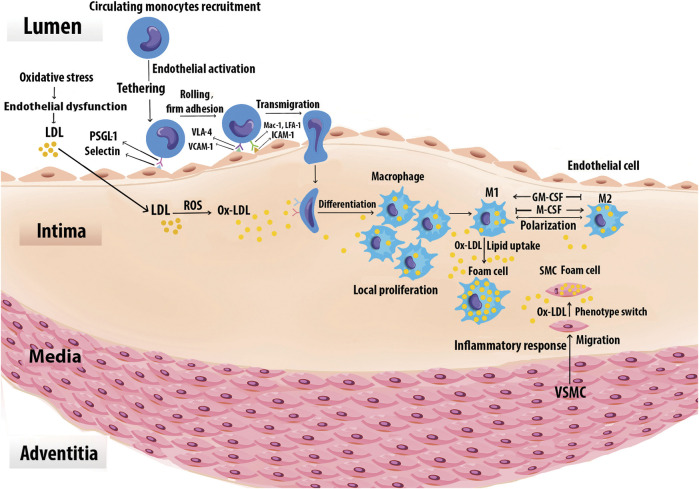
FIGURE 3.
Foam cell formation. Monocytes are recruited to the vascular arginase wall in response to Ox-LDL. Specific adhesion molecules such as the selectins, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1 are expressed on the surface of activated vascular ECs, mediate monocyte adhesion. Once adherent, the monocytes enter the intima and differentiate into Mφs. The differentiation process may be mediated by GM-CSF and M-CSF. Local Mφ proliferation contributes to lesion growth. Upon extensive uptake of Ox-LDL via SRs, Mφs are ultimately turned into foam cells. Chemoattractants, growth factors, and cytokines also promote SMC proliferation, uptake of Ox-LDL, and eventually conversion to foam cells. Foam cells derived from SMCs together with those derived from Mφs generate the fatty lesion.