Figure 4.
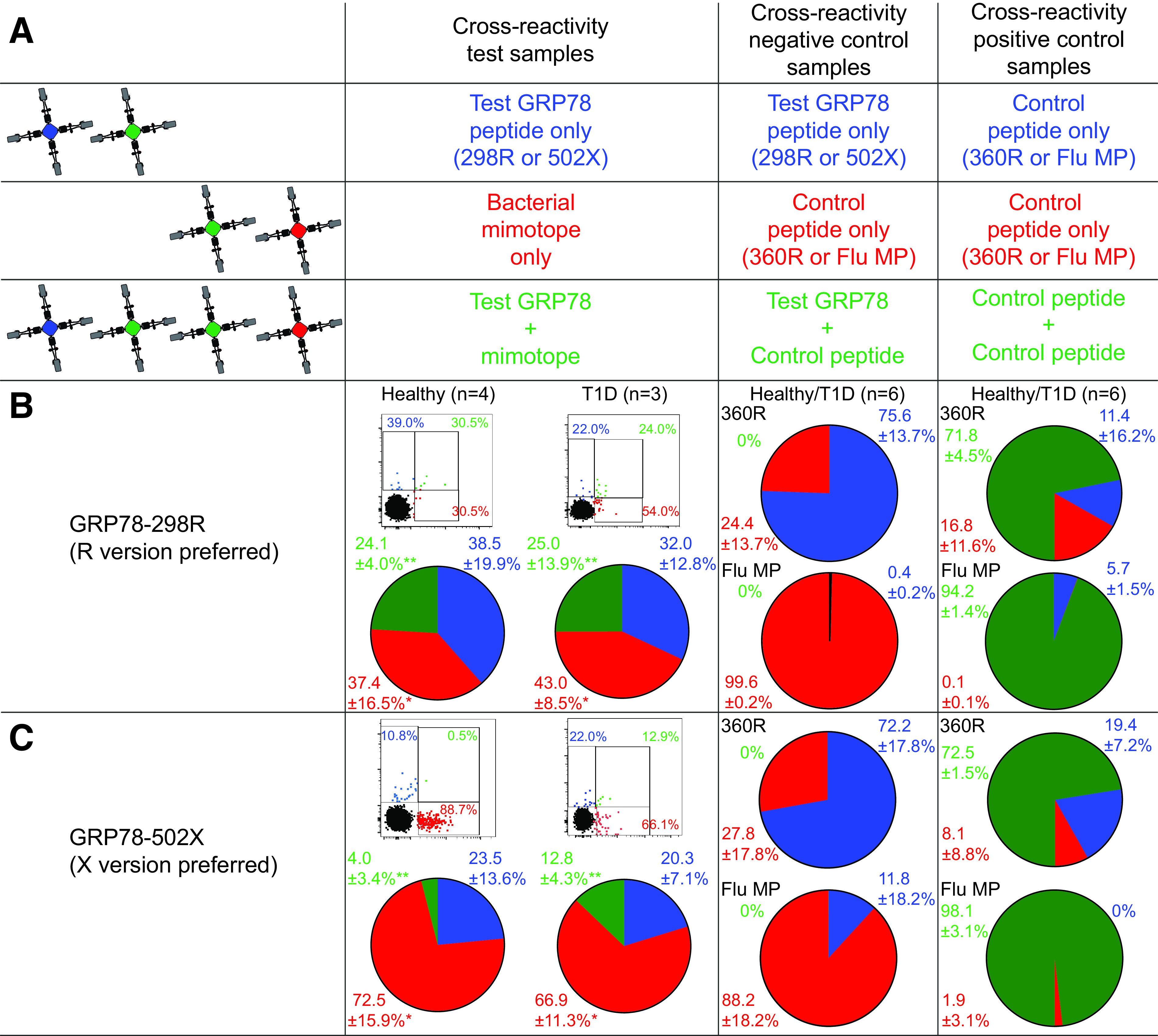
GRP78 peptides preferentially recognized in their native R version are cross-reactive with gut bacterial mimotopes. A: Schematic view of the combinatorial analysis applied. With a strategy similar to the one described in Fig. 2A, three PBMC aliquots were stained with two MMr pairs sharing one fluorochrome (green). With gating on double or triple MMr+ events, cells recognizing only one peptide or both are visualized, respectively. B and C: Representative dot plots and cumulative results from healthy donors and donors with type 1 diabetes (pie charts) obtained for GRP78-298R (B), GRP78-502X (C), and their respective peptide mimotopes. The first column shows the results obtained on the first T cell aliquot (test sample) by crossing MMrs loaded with GRP78 and bacterial mimotope peptides, with the T cell fraction recognizing both highlighted in green. The second column displays the cross-reactivity between GRP78 peptide and GRP78-360R or Flu MP58–66 epitope (negative control; second PBMC aliquot). The third column displays the cross-reactivity between GRP78-360R or Flu MP58–66 peptides charged on both MMr pairs (positive control; third PBMC aliquot). Dot plots and pie charts display the percentage of MMr+ cells binding either MMr (blue or red) or both (green). In dot plots, the MMr‒ population is displayed in black for visualization of the position of MMr+ events relative to it. **P = 0.016 and *P = 0.031 by Wilcoxon signed rank test for the comparison of cross-reactive (green) fractions and of mimotope-reactive (red) fractions, respectively, between GRP78-298R and -502X (pooled healthy donors and donors with type 1 diabetes). T1D, type 1 diabetes.
