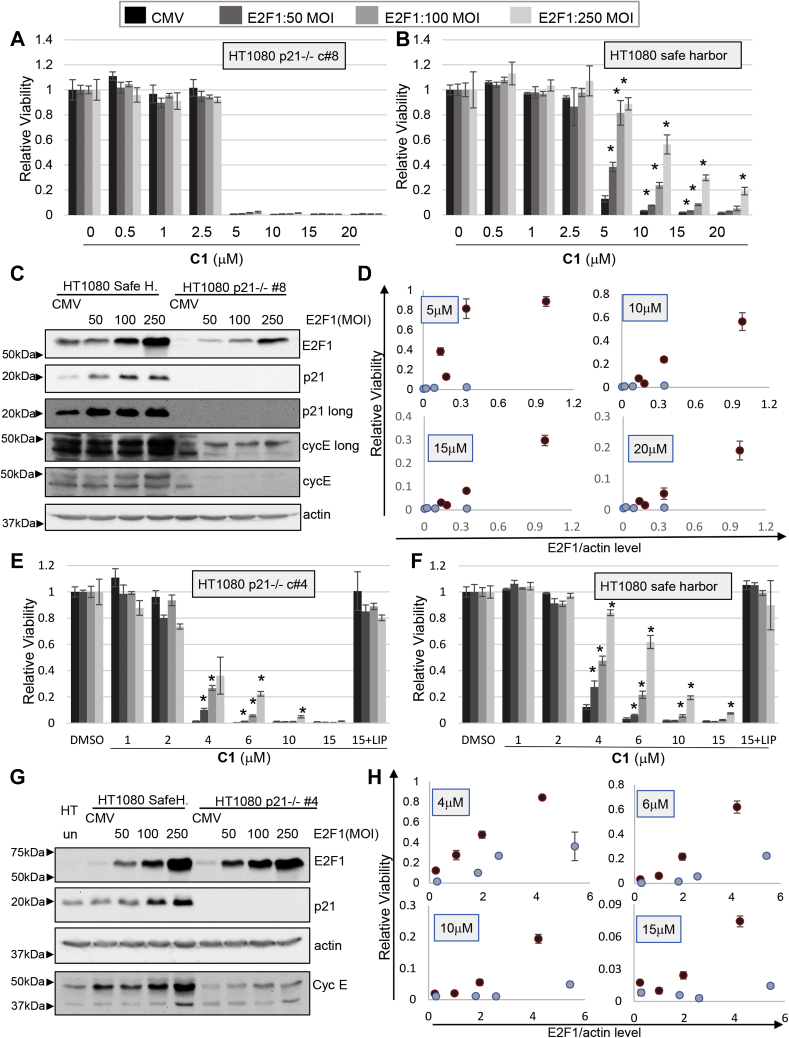
Figure 11.
E2F1 inhibition of ferroptosis requires p21. HT1080 cells lacking p21 or controls cells expressing the safe-harbor gRNA were infected with recombinant adenoviruses to express E2F1. Two KO clones ([clone #8: A–D] and [clone #4: E and F]) were analyzed. Ferroptosis was induced by exposure to CETZOLE 1 (C1), which was added 48 h after virus infection. Cell viability was determined 48 h after adding CETZOLE 1 using methylene blue staining. Viability is presented as average relative viability + SD. ∗p < 0.05 when compared with CMV-infected cells at the same dose of CETZOLE 1. Multiplicity of infection (MOI) is indicated. A and B, viability in response to CETZOLE 1 and E2F1 expression in safe-harbor and clone #8 cells. C, Western blot analysis shows the level of p21, E2F1, cyclin E, and actin proteins upon E2F1 transduction in p21 −/− clone #8 cells. D, relative viability is plotted as a function of E2F1 expression level determined by quantifying Western blot signals. Each symbol represents average viability and E2F1 expression values at a particular MOI. Clone #8 cells (blue symbols) express less E2F1 than safe harbor cells (red symbols) so viability should be compared at similar E2F1 values and not equal MOI. Error bars represent the SD of cell viability of each dose. E and F, viability analysis in safe-harbor and clone #4 cells. Liproxstatin-1 (0.25 μM) was added along 15 μM CETZOLE 1 to assess the contribution of lipid oxidation to cell death. G, Western blot analysis after E2F1 transduction in clone #4 cells. H, plot of viability versus E2F1 expression levels measured from Western blots. Clone #4 cells (blue symbols) express similar levels of E2F1 as safe-harbor cells (red symbols) when infected at the same viral MOI.