Figure 1.
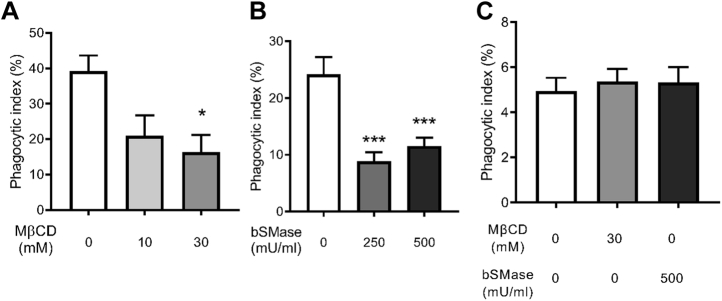
Cholesterol and sphingomyelin are important for antibody-mediated phagocytosis.A, macrophages (MH-S) treated with either 10 or 30 mM methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (MβCD) were coincubated with antibody-opsonized Cryptococcus neoformans H99 at a 1:1 ratio and allowed to interact for 2 h. Cells were then fixed and stained with Giemsa, and phagocytic index was calculated by microscopic observation (n = 4). B, macrophages (MH-S) treated with either 250 or 500 mU/ml bacterial sphingomyelinase (bSMase) were coincubated with antibody-opsonized C. neoformans H99 at a 1:1 ratio and allowed to interact for 2 h. Cells were then fixed and stained with Giemsa, and phagocytic index was calculated by microscopic observation (n = 3). C, macrophages (MH-S) treated with 30 mM MβCD or 500 mU/ml bSMase were coincubated with complement serum-opsonized C. neoformans H99 at a 1:1 ratio and allowed to interact for 3 h. Cells were then fixed and stained with Giemsa, and phagocytic index was calculated by microscopic observation (n = 4). Error bars represent the SEM, and statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared with the untreated control. All p values were adjusted for multiplicity.