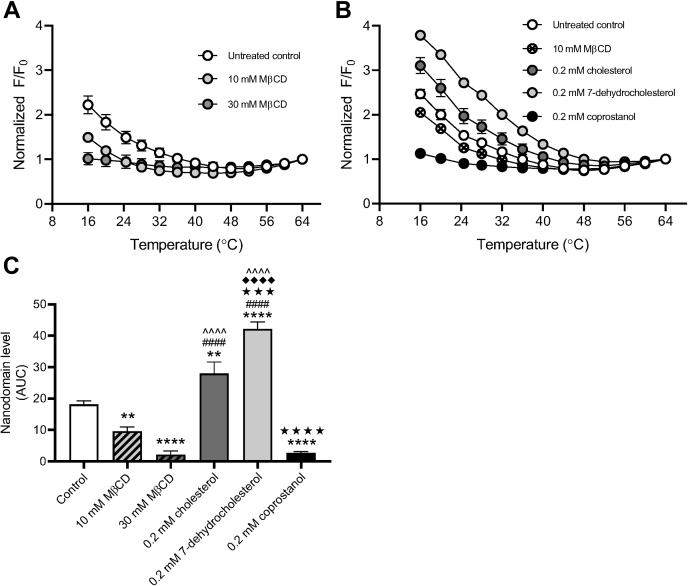
Figure 4.
Repletion with raft-altering sterols affects nanodomain stability.A, macrophages (MH-S) were pretreated with either 10 or 30 mM methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (MβCD) to deplete cholesterol. Monolayers were then washed and subject to giant plasma membrane vesicle formation using 25 mM paraformaldehyde (PFA) and 2 mM DTT. Nanodomain stability was assessed via FRET with diphenylhexatriene (DPH) as the FRET donor and octadecyl rhodamine B (ODRB) as the FRET acceptor. The ratio of DPH fluorescence intensity in the presence versus absence of ODRB was calculated (F/F0). F/F0 values were normalized to the final F/F0 value at 64 °C (n = 3). B, macrophages were pretreated with 10 mM MβCD to deplete cholesterol and then washed and incubated with 2.5 mM MβCD loaded with 0.2 mM of indicated sterol. Monolayers were then washed and subject to giant plasma membrane vesicle formation using 25 mM PFA and 2 mM DTT. Nanodomain stability was assessed via FRET with DPH as the FRET donor and ODRB as the FRET acceptor. The ratio of DPH fluorescence intensity in the presence versus absence of ODRB was calculated (F/F0). F/F0 values were normalized to the final F/F0 value at 64 °C (n = 3). C, relative domain levels were estimated using the polynomial fits from (A) and (B) as described under the Experimental procedures section. Error bars represent SEM. Detectable nanodomains were compared using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 compared with the untreated control, ####p < 0.0001 compared with 10 mM MβCD, ˆˆˆˆp < 0.0001 compared with 30 mM MβCD, ★★★p < 0.001, ★★★★p < 0.0001 compared with 0.2 mM cholesterol, and ◆◆◆◆p < 0.0001 compared with 0.2 mM coprostanol. All p values were adjusted for multiplicity.