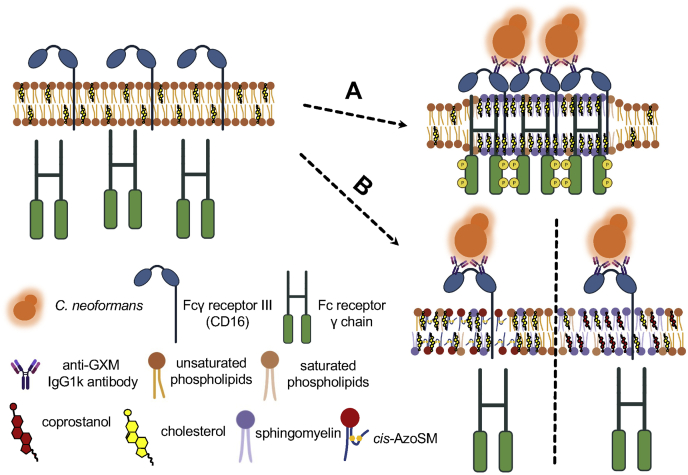
Figure 9.
Cholesterol- and sphingomyelin (SM)-rich plasma lipid rafts are important for Fcγ receptor–mediated phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans by macrophages. Upon binding IgG-based immune complexes comprised of antiglucuronoxylomannan (GXM) antibody-opsonized C. neoformans, Fcγ receptor III (CD16) localizes to the plasma lipid rafts. A, when lipid rafts are enriched with raft-forming sterols (i.e., cholesterol and 7-dehydrocholesterol; only cholesterol shown for simplicity) or SM (i.e., trans-AzoSM; only endogenous SM shown for simplicity), the Fc receptor γ chain is properly phosphorylated to initiate the signaling cascade associated with phagocytosis. B, when lipid rafts are enriched with raft-inhibiting sterols such as coprostanol (right) or raft-disrupting SM, cis-AzoSM (left), Fc receptor γ chain is not properly phosphorylated.