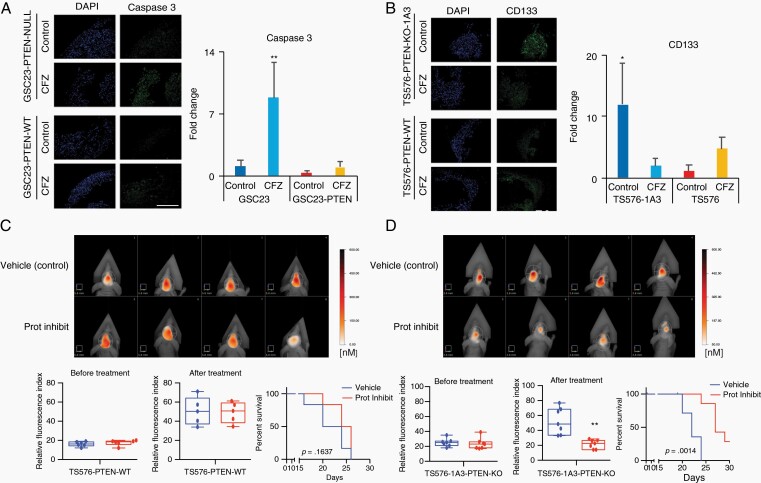
Fig. 6.
Proteasome inhibition induces cell death in GBM-organoids and inhibits intracranial tumor growth. A and B, Left panels, representative immunofluorescence staining of active caspase-3 (A) or, stem-cell marker, CD133 (B) in PTEN-deficient and -expressing GBM-organoids before and after treatment with 100 nM carfilzomib (CFZ) per 48 hours. DAPI, nuclear staining. Right panels, bar plot quantification of fluorescent signal intensities (n = 2-3 organoids and 5-10 fields, two-way ANOVA, multiple comparisons, *P < .05, **P < .01). Scale bar length 500 μm. C and D, Upper panels, representative FMT images of mice engrafted with TS576 PTEN-WT (C) or TS576-1A3 PTEN-null (D) GSCs and untreated (vehicle) or treated with proteasome inhibitor (5 mg/kg daily for 2 weeks). Bottom panels, tumor burden (relative fluorescence quantification) before (left) and after drug treatment (middle) (n = 5-7 animals per group, t-test comparison, **P < .01). Error bars represent the SEM from different independent experiments. Kaplan-Meier survival plots of mice treated with either a proteasome inhibitor (red) or vehicle only control (blue) (right). Abbreviations: DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GNM, glioblastoma; GSCs, glioblastoma stem cells; Prot Inhibit, proteasome inhibitor.