Figure 2.
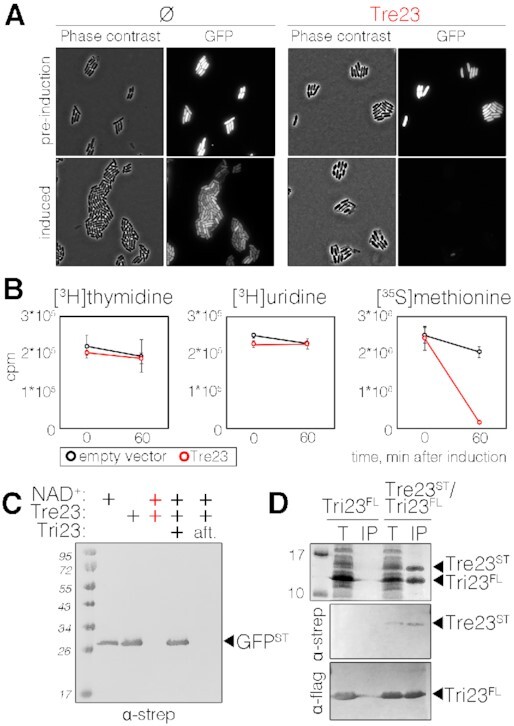
Tre23 inhibits protein synthesis. (A) Phase contrast and fluorescence microscopy recordings of E. coli cells constitutively producing short-lived green fluorescent protein (GFP-LVA) and the Tre23 toxin from the low-copy number pNDM220 vector, before and 100 min post toxin induction. Cells bearing the empty pNDM220 vector (Ø) were used as control. (B) Replication, transcription and translation rates before (time 0) and 60 min after the induction of Tre23 toxin from pNDM220 vector (red line) as compared to control carrying empty vector (black line) were measured by the incorporation (in count per minute, cpm) of [3H] thymidine, [3H] uridine and [35S] methionine, respectively. (C) Coupled in vitro transcription-translation reaction. In vitro transcription/translation of the Strep-tagged GFP reporter protein was estimated by immunodetection. Reactions were supplemented with NAD+, Tre23 and Tri23, as indicated. In the last reaction, Tri23 was added 1 h after incubating the reaction with Tre23 (aft) and reaction proceeded for 2 h. (D) Tre23-Tri23 co-purification. Total cell lysates of E. coli BL21(DE3) cells producing FLAG-tagged Tri23 (Tri23FL) alone or co-producing Strep-tagged Tre23 (Tre23ST) (T) were subjected to purification on streptactin agarose beads followed by immunoprecipitation on anti-FLAG affinity gel (IP). Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained by Coomassie (upper panel) or immunodetected using anti-Strep and anti-FLAG antibodies (middle and bottom panels, respectively).
