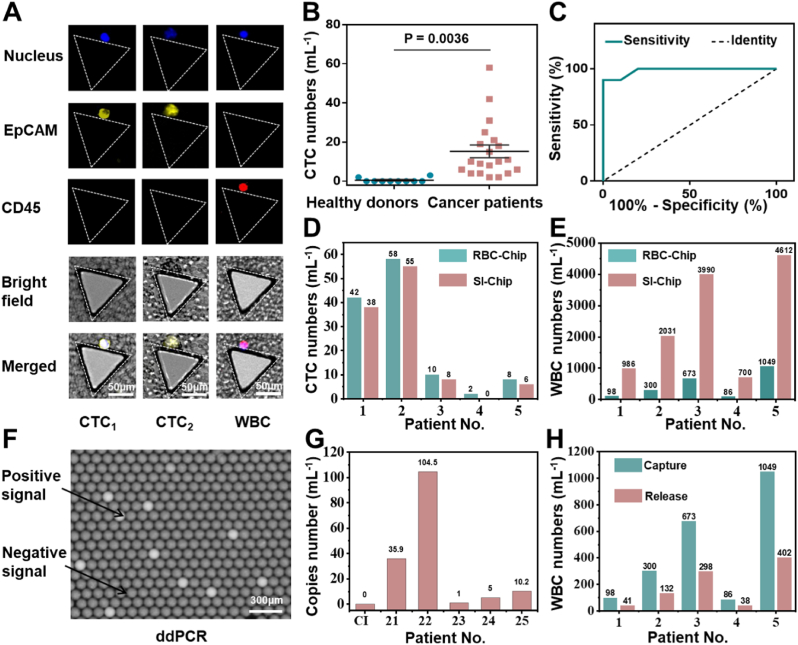
Fig. 6.
Detecting CTCs in clinical samples from cancer patients with RBC-Chip. (A) Micrographs of representative CTCs and residual WBCs from patients' blood. (B) Enumeration of CTCs in 1 mL blood samples from 20 colon cancer patients and 10 healthy donors. (C) ROC analysis of CTC numbers between the cancer patients group and healthy donors group. (D) Numbers of CTCs captured by RBC-Chip and SI-Chip, respectively, from 1 mL of cancer patient blood. (E) Residual WBC numbers of RBC-Chip and SI-Chip, respectively, from 1 mL of cancer patient blood. (F) Image of ddPCR result. The bright droplets indicate the existence of the KRAS mutant gene, and the dark droplets indicate the absence of the KRAS mutant gene. (G) The KRAS mutation results of clinical samples or RBC lysis buffer (control group, Cl) by ddPCR. (H) Residual WBC numbers before and after CTCs release, respectively, from 1 mL of cancer patient blood.