Figure 3.
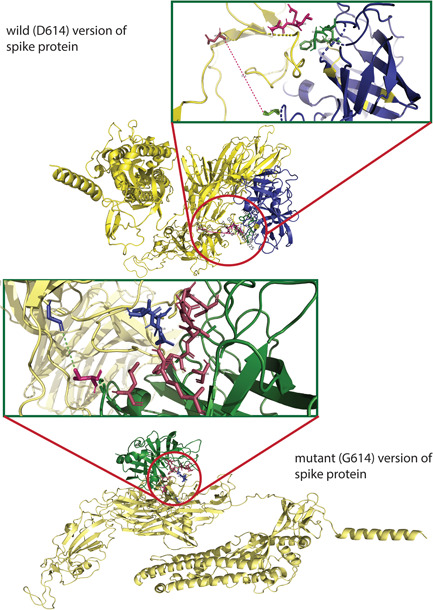
The molecular docking of wild and mutant with elastase‐2. Both the (upper figure) wild (D614) and (lower figure) mutant (G614) version of S protein was shown in golden color, whereas the elastase‐2 docked to D614 and G614 in blue and green color, respectively. The enlarged views of the docked site were shown in separate boxes. (A) The possible docked residues (stick model) on the wild S protein (warm pink) and elastase‐2 (green) are 618(Thr)−619(Glu)−620(Val) and 198(Cys)−199(Phe)−225:227 (Gly, Gly, Cys), respectively. The aspartic acid at 614 is 17.3°A far away from the valine (101), apparently the nearest aa of elastase‐2 to the cleavage site (615–616). (B) The possible interacting residues (stick model) on the mutant S protein (blue) and elastase‐2 (warm pink) are 614(Gly)−618(Thr)−619(Glu)−620(Val) and 101(Val)−103(Leu)−181(Arg)−222:227(Phe, Val, Arg, Gly, Gly, Cys), and 236 (Ala), respectively. In this case, the glycine at 614 is 5.4°Afar from the valine (101), the nearest aa of elastase‐2 to the cleavage site (615–616)
