Figure 2.
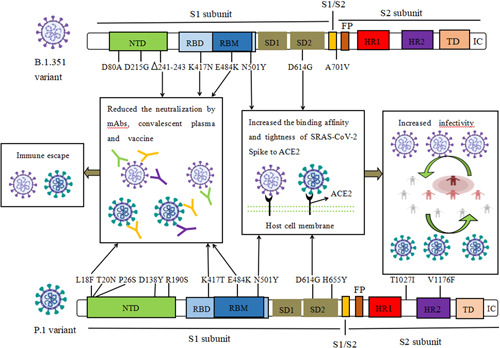
The biological characteristics of key amino acid mutations of Spike in B.1.351 and P.1 variant. Mutations including N501Y, D614G could increase the binding affinity and binding tightness of SARS‐CoV‐2 spike to hACE2 receptor, and result in increasing the infectivity of B.1.1.7 and B.1.617.2 variant. 241‐243del, L18F, K417N/T, E484K mutations generated resistance to the neutralization activity of mAbs, convalescent plasma, and postvaccination serum against B.1.351 and P.1 variant. del, deletion; FP, fusion peptide; HR1, heptad repeat 1; HR2, heptad repeat 2; IC, intracellular domain; NTD, N‐terminal domain; RBD, receptor‐binding domain; RBM, receptor binding motif; SD1, subdomain 1; SD2, subdomain 2; TD, transmembrane domain
