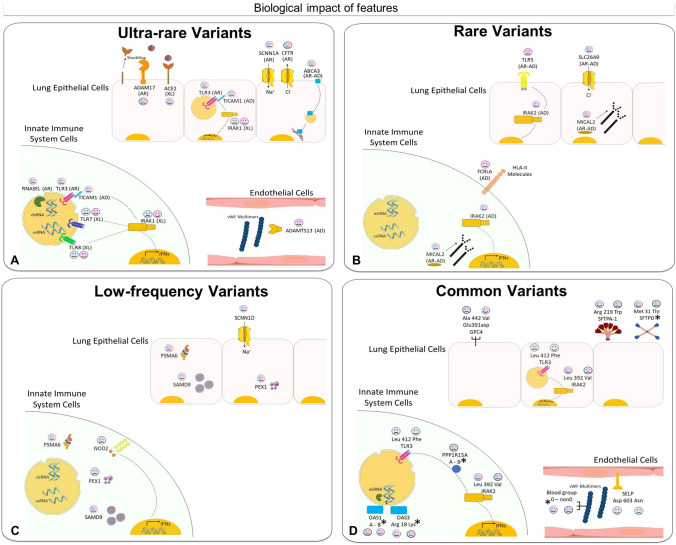
Fig. 2.
Biological impact of ultra-rare, rare, low-frequency, and common features. Examples of ultra-rare (A), rare (B), low-frequency (C), and common (D) features are illustrated in panel A–D. The complete list of features is presented in Supplementary Tables 3–6. 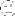 = contributing to COVID-19 severity;
= contributing to COVID-19 severity; 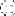 = contributing to COVID-19 mildness. Pink faces = contributing to females only; blue faces = contributing to males only; pink/blue faces = contribution in both sexes. In parentheses: AD = autosomal dominant inheritance; AR = autosomal recessive inheritance; XL = X-linked recessive inheritance. A Ultra-rare mutations in the RNA sensor TLR7, TLR3, and TICAM1 (encoding TRIF protein), already reported associated with XL, AR and AD inheritance (Zhang et al. 2020a; Van der Made et al. 2020; Fallerini et al. 2021a; Solanich et al. 2021) impair interferon (IFNs) production in innate immune system cells. Mutations in TLR8, as well as of the signal transducer IRAK1 also impair interferon production. The specific location of TLR7/8 and IRAK1 (on the X chromosome) as well as X-inactivation escaping are responsible for opposite effects in males and females. Mutation in RNASEL impair the antiviral effect of the gene. In lung epithelial cells, ACE2 ultra-rare variants (on the X chromosome) exert protective effects (probably) due to lowering virus entrance, while ultra-rare variants in ADAM17 (might) reduce the shedding of ACE2 and induce a severe outcome. The same is true for CFTR and SCNN1A (encoding ENaCA protein and involved in a CFTR-related physiological pathway), and the lipid transporter ABCA3 (Baldassarri et al. 2021b).Mutations of ADAMTS13 in vessels reduce the cleavage of the multimeric von Willebrand Factor (VWF), leading to thrombosis; B) Rare variants of the estrogen regulated TLR5 are associated with severity in females. Rare variants of the CFTR-related SLC26A9 are associated with severity in both sexes. This ion transporter has three discrete physiological modes: nCl(–)-HCO(3)(–) exchanger, Cl(–) channel, and Na(+)-anion cotransporter. Other examples of rare mutations associated with severity are the NK and T cell receptor FCRL6, IFN signal transducer IRAK2, and the actin depolymerization MICAL2; C low-frequency variants in another CFTR-related gene, SCNN1D (encoding for ENaCD protein) are associated with mildness, while rare variants in the following genes are associated with severity: cargo protein SPMA6, vesicle formation PEX1, inflammatory protein NOD2 (CARD15); D A number of coding polymorphisms, indicated with an asterisk, are in LD with genomic SNPs already associated with COVID-19 (The complete list is presented in Supplementary Table 11) (Severe Covid-19 GWAS Group (2020; Pairo-Castineira et al. 2020). In some cases, such as the case of SFTDP, the genomic SNP is the coding polymorphism itself. Of note are the genes of surfactant proteins associated with severe disease: SFTDP gene encoding for SP-D protein and SFTPA1 gene encoding for SP-A protein; the signal transducer, PPP1R15A gene encoding for GADD34 protein. OAS1 and OAS3 related to RNA clearance of RNASEL (reported in panel A as having ultra-rare mutations; included here should also be the already reported TLR3412 (Croci et al. 2021); the already reported SELP603 related to thrombosis (Fallerini et al. 2021a). Note: OAS1 haplotype A = c.1039-1G>A (Wickenhagen et al. 2021), (p.(Gly162Ser)), (p.(Ala352Thr)), (p.(Arg361Thr)), (p.(Gly397Arg)), (p.(Thr358Profs*26)). OAS1 haplotype B = haplotype without the variant combination in haplotype A
= contributing to COVID-19 mildness. Pink faces = contributing to females only; blue faces = contributing to males only; pink/blue faces = contribution in both sexes. In parentheses: AD = autosomal dominant inheritance; AR = autosomal recessive inheritance; XL = X-linked recessive inheritance. A Ultra-rare mutations in the RNA sensor TLR7, TLR3, and TICAM1 (encoding TRIF protein), already reported associated with XL, AR and AD inheritance (Zhang et al. 2020a; Van der Made et al. 2020; Fallerini et al. 2021a; Solanich et al. 2021) impair interferon (IFNs) production in innate immune system cells. Mutations in TLR8, as well as of the signal transducer IRAK1 also impair interferon production. The specific location of TLR7/8 and IRAK1 (on the X chromosome) as well as X-inactivation escaping are responsible for opposite effects in males and females. Mutation in RNASEL impair the antiviral effect of the gene. In lung epithelial cells, ACE2 ultra-rare variants (on the X chromosome) exert protective effects (probably) due to lowering virus entrance, while ultra-rare variants in ADAM17 (might) reduce the shedding of ACE2 and induce a severe outcome. The same is true for CFTR and SCNN1A (encoding ENaCA protein and involved in a CFTR-related physiological pathway), and the lipid transporter ABCA3 (Baldassarri et al. 2021b).Mutations of ADAMTS13 in vessels reduce the cleavage of the multimeric von Willebrand Factor (VWF), leading to thrombosis; B) Rare variants of the estrogen regulated TLR5 are associated with severity in females. Rare variants of the CFTR-related SLC26A9 are associated with severity in both sexes. This ion transporter has three discrete physiological modes: nCl(–)-HCO(3)(–) exchanger, Cl(–) channel, and Na(+)-anion cotransporter. Other examples of rare mutations associated with severity are the NK and T cell receptor FCRL6, IFN signal transducer IRAK2, and the actin depolymerization MICAL2; C low-frequency variants in another CFTR-related gene, SCNN1D (encoding for ENaCD protein) are associated with mildness, while rare variants in the following genes are associated with severity: cargo protein SPMA6, vesicle formation PEX1, inflammatory protein NOD2 (CARD15); D A number of coding polymorphisms, indicated with an asterisk, are in LD with genomic SNPs already associated with COVID-19 (The complete list is presented in Supplementary Table 11) (Severe Covid-19 GWAS Group (2020; Pairo-Castineira et al. 2020). In some cases, such as the case of SFTDP, the genomic SNP is the coding polymorphism itself. Of note are the genes of surfactant proteins associated with severe disease: SFTDP gene encoding for SP-D protein and SFTPA1 gene encoding for SP-A protein; the signal transducer, PPP1R15A gene encoding for GADD34 protein. OAS1 and OAS3 related to RNA clearance of RNASEL (reported in panel A as having ultra-rare mutations; included here should also be the already reported TLR3412 (Croci et al. 2021); the already reported SELP603 related to thrombosis (Fallerini et al. 2021a). Note: OAS1 haplotype A = c.1039-1G>A (Wickenhagen et al. 2021), (p.(Gly162Ser)), (p.(Ala352Thr)), (p.(Arg361Thr)), (p.(Gly397Arg)), (p.(Thr358Profs*26)). OAS1 haplotype B = haplotype without the variant combination in haplotype A