FIGURE 1.
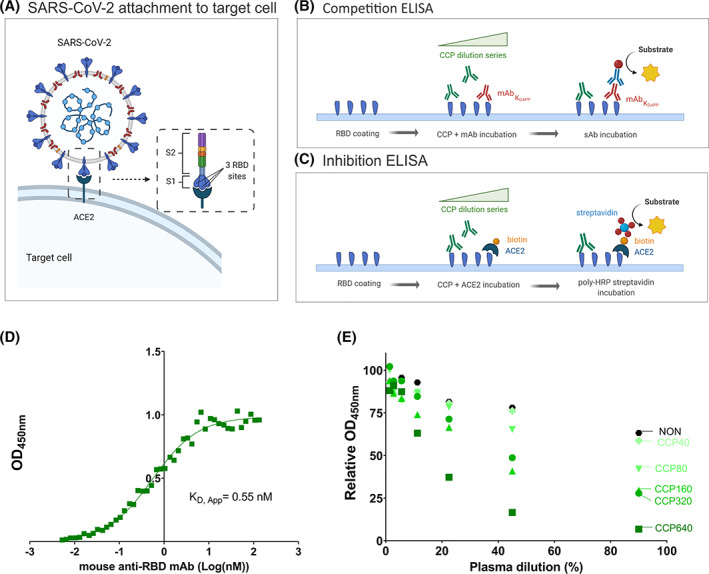
ELISA design to measure neutralizing antibodies in CCP. (A) The adhesion of SARS‐CoV‐2 to the target cell is mediated by the interaction between Spike protein (S1 and S2) of SARS‐CoV‐2 (composed of 3 RBD sites) with the ACE2 host receptor. (B) Competition ELISA measuring the amount of neutralizing murine anti‐RBD mAb (red) binding to immobilized RBD in the presence of varying concentrations of CCP. Detection of bound mAb is with peroxidase labeled secondary anti‐mouse antibody (blue). (C) Inhibition ELISA measuring the amount of biotinylated (orange) ACE2 binding to immobilized RBD in the presence of varying concentrations of CCP (green). Detection of bound ACE2 is with peroxidase labeled streptavidin. (D) For selection of the optimal mAb concentration, binding of mAb to immobilized RBD was investigated. Absorbance (OD450nm) as a function of increasing amounts of mAb (log transformed concentration in nM) indicates saturable binding with a KD,App of 0.55 nM. (E) Results of the competition ELISA using a selected series of CCP of known PRNT50 titer as indicated by color coding. The black dots assigned “NON” were from a pool of non‐immune plasma (n = 15) as a negative control. All 7‐step titrations were conducted in triplicate and mean values are given [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
