Figure 1.
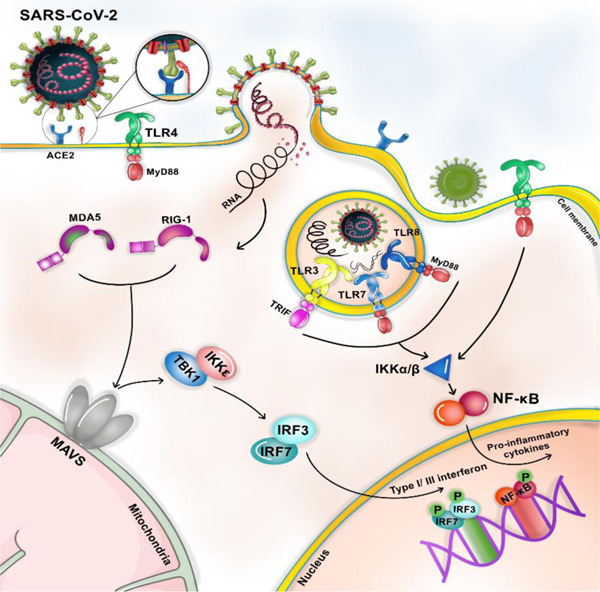
Innate immune response In the first step, infectious viral particles (PAMPs) were sensed through PRRs. SARS‐CoV‐2 is detected through endosomal PRRs including TLR 3, 7, 8, and 9 and/or through cytoplasmic PRRs such as MDA5 and RIG‐1. Moreover, the virus can be sensed through TLR4, which is localized in the cell membrane. Following TLRs activation, NF‐'kB's transcription factor induces inflammatory cytokines, whereas activated MDA5 and RIG‐1 recruit IRF3 and IRF7 for interferon production. When interferon binds its receptor, IFRAR1/2, an IFN‐induced signaling pathway is initiated, resulting in the recruitment of JAK‐1 and TYK. JAK‐1 and TYK activation trigger the phosphorylation of the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1 and 2, respectively. Subsequently, an IFN‐stimulated gene factor 3 (ISGF3) complex is formed, containing STAT1, STAT2, and IRF‐9. This complex translocated to the nucleus and increases the expression of IFN‐stimulated genes (ISGs). ISGs translation and posttranslational modification trigger antiviral action interferons, including Inhibition of mRNA inhibition, RNA degradation, RNA editing, and the initiation of T cell response, and NO synthesis. IFN, interferon; IRF, IFN regulatory factor; MDA, melanoma differentiation‐associated protein; mRNA, messenger RNA; PRRs, pattern recognition receptors; RIG, retinoic acid‐inducible gene‐1‐like receptor; SARS‐CoV‐2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TLR, Toll‐like receptor
