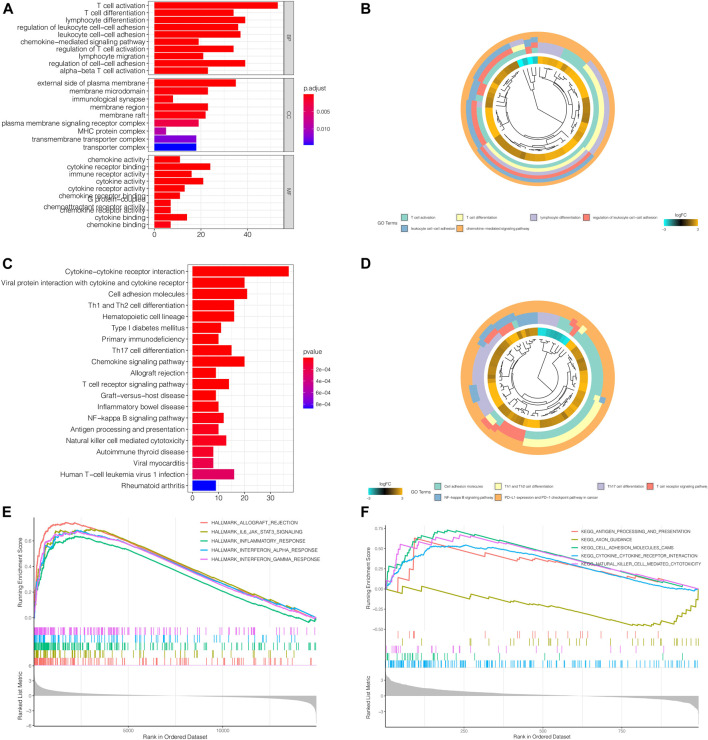
FIGURE 6.
GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis revealed that the differential genes between high risk and low risk groups were strongly correlated with immune response. (A,B) GO Enrichment analysis revealed that, biological processes like T cell activation and differentiation, lymphocyte differentiation and leukocyte cell-cell adhesion; molecular functions such as chemokine activity, cytokine activity, immune receptor activity, as well as cytokine receptor activity were enriched in differential genes between the high-risk group and the low-risk group. The enriched genes were mainly concentrated in the external side of the plasma membrane, which was in line with our findings that the differential genes were correlated immune response. (C,D) KEGG analysis revealed a more specific picture of which pathways were enriched between the two groups. Not only was Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation related to the risk model, but PD-1 and PD-L1 activity was also concerned. However, further studied are still needed to validate the relationship between the relationship with our model and immune response. (E) GSEA showed that immune-related functional gene sets were mainly enriched in the high-risk group, including allograft rejection, IL6-JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway, inflammatory response, interferon-alpha response, interferon-gamma response. (F) 2,483 immune-related genes were downloaded from IMMPORT database. Through GSEA analysis, we found that these immune-related genes are mainly enriched in antigen processing and presentation, cell adhesion molecules, cytokine receptor interactions, and ccytotoxicity mediated by natural killer cells in the high-risk group. Axon guidance was the main enrichment pathway in the low-risk group.