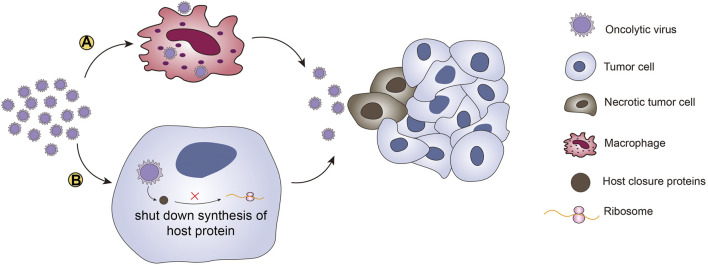
FIGURE 3.
Therapeutic barriers of oncolytic viruses. There are two main barriers to the induction of antitumor effects by oncolytic viruses. (A) Macrophages can directly capture viruses in organs such as the liver. Macrophages reduce the virus titer and the antitumor effects through phagocytosis. (B) The other barrier for oncolytic viruses is blockade of host protein synthesis. Oncolytic viruses encode host closure proteins that can shut down synthesis of host proteins, destroy pre-existing polysomes, degrade host mRNAs, and interfere with the production of viral offspring. This “host shutoff” is not conducive to virus replication or the expansion of neoantigen-reactive CTLs.