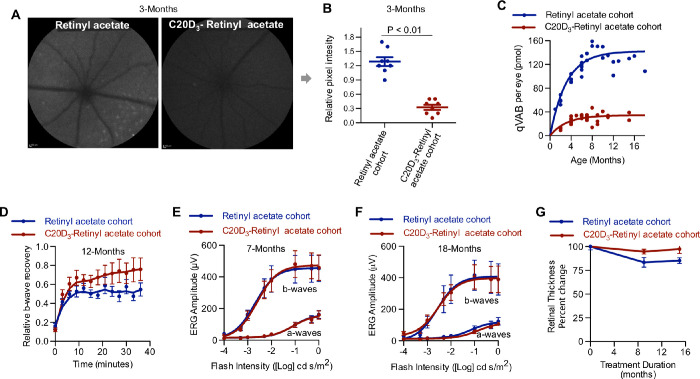
Figure 3.
C20D3-Vitamin A Prevents the Prodromal Phase of Retinal Degenerations. (A) Representative quantitative fundus autofluorescence (AF) images of 3-month-old Abca4−/−/Rdh8−/− mice administered a diet containing vitamin A as either retinyl acetate or C20D3-retinyl acetate. (B) Average (with SEM) AF intensity of the retinas of mice described in panel A. Each spot corresponds to the AF intensity of a single eye. Eight eyes of eight different animals per cohort were imaged (n = 8). P-value is from a two-sided, unpaired T-test. (C) The qVAB (A2E, iso-A2E, and oxo-A2E) in mice described in panel A. Each point represents between 5 and 10 pooled eyes. (D) Average (SEM) ERG b-wave recoveries following light exposure in ∼12-month-old Abca4−/−/Rdh8−/− mice administered a diet containing retinyl acetate (n = 13 eyes, blue curve, recovered a mean and SD of 71% ± 0.7% after 30 minutes of dark-adapted maximum b-wave) or C20D3-retinyl acetate (n = 12 eyes, red curve, recovered 53 ± 0.5%, P = 0.01, two-sided F-test). (E and F) ERG dose-response curves (average with SEM) for the cohorts of dark-adapted Abca4−/−/Rdh8−/− mice described in panel A at seven months (E, retinyl acetate: n = 16 eyes; C20D3-retinyl acetate: n = 19 eyes) and 18 months of age (F, retinyl acetate: n = 12 eyes; C20D3-retinyl acetate: n = 12 eyes). (G) Percent change in retinal thickness (RPE and neuroretina) from baseline (3 months of age) in mice described in panel A, measured 1 mm from either side of the optic nerve head. Averages and SEM are shown. C20D3-retinyl acetate: n = 6 at three months, n = 14 at 12 months, and n = 4 at 18 months. Retinyl acetate: n = 5 at 3 months, n = 5 at 12 months, and n = 10 at 18 months. Each eye was from a different animal.