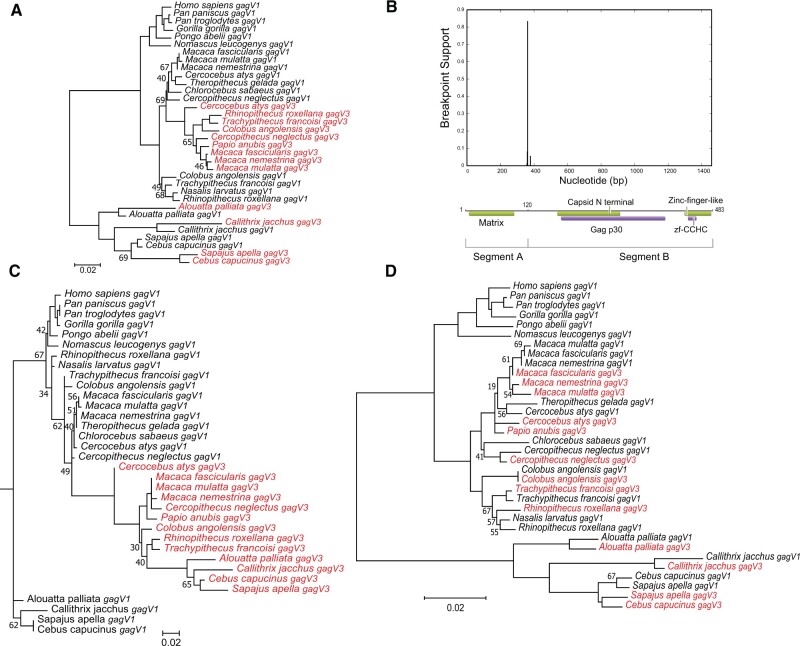
Fig. 7.
Evolution of gagV1 and gagV3 in Simiiformes. (A) gagV1 and gagV3 ORFs from the indicated primate species were aligned (supplementary data set 3, Supplementary Material online) and a maximum likelihood tree was generated using RaxML with 500 replicates. Bootstrap values that are below 70 are shown at the relevant nodes. The tree was midrooted. gagV3 genes are shown in red. (B) Plot with the model-averaged support (y-axis) for recombination breakpoints as calculated by GARD is shown above the human GagV1 protein. Nucleotide position of human gagV1 is indicated on the x-axis. Domains predicted via SupFam (green) and Pfam (purple) are indicated on GagV1. Maximum likelihood trees are generated using RaxML with aligned gagV1 and gagV3 nucleotide sequences from (C) GARD segment A (first 360 nucleotides) or (D) GARD segment B. Bootstrap values that are below 70 are shown at the relevant nodes. The tree was midrooted. gagV3 genes are shown in red.