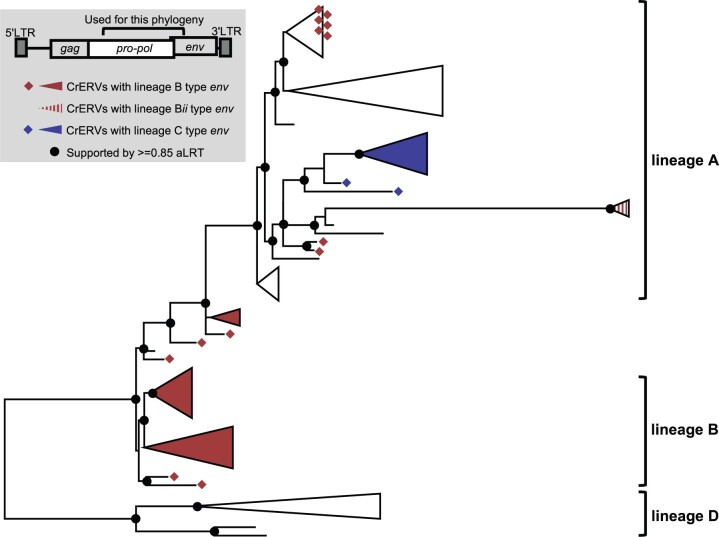
Fig. 3.
Recombination among CrERVs. Shown is a maximum likelihood phylogeny based on a region spanning a portion of pol to 5′env (JN592050: 4,422–7,076). Taxa used are a subset of full-length nonrecombinant CrERVs representing the four lineages shown in figure 2 and CrERVs with a recombinant signature containing a Lineage B env. Supported nodes (aLRT≥0.85) are represented by black dots on the backbone of the tree. Lineage designation is assigned to supported branches based on the nonrecombinant CrERV. Over this interval, Lineage B CrERVs are found as a sister group to Lineage A CrERV but some CrERV containing a prototypical Lineage B env are dispersed among Lineage A CrERV. Note that in this interval Lineage C CrERVs cluster with Lineage A CrERVs.