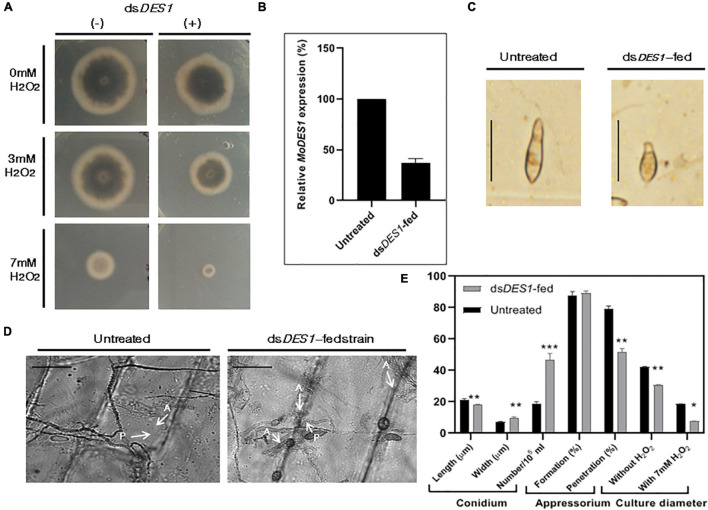
FIGURE 4.
Assessment of ROS-scavenging activity, morphological traits, and target transcripts in the in vitro dsDES1- fed strain. (A) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) sensitivity assay of dsDES1-fed and untreated strains of wild-type B157. The dsDES1-fed and dsDES1-untreated strains were grown on CM plates with 0, 3, and 7 mM H2O2, and average growth diameter of the cultures was recorded from 5- to 10-day-old plates in triplicates. The experiment was repeated twice. (B) Relative MoDES1 expression in the dsDES1-fed strain with respect to the untreated strain 72 hpt. The reactions were set up in triplicates, and MoACTIN was used as internal control. (C) The dominant morphological deformity in a major fraction of conidia isolated from the dsDES1-fed strain. For size reference, a 20-μm scale has been used. (D) Penetration potential of germinated appressoria among the untreated and dsDES1-fed strain, on onion epidermal peel. A 50-μm scale has been used for size- reference. Three replicates were used, and at least 50 conidia were assessed in each category. (E) Comparison of phenotypic parameters between untreated and dsDES1-fed strain. Error bars represent standard deviation, and *, **, *** denote statistical significance at the P ≤ 0.05, P ≤ 0.01, and P ≤ 0.001 level, respectively.