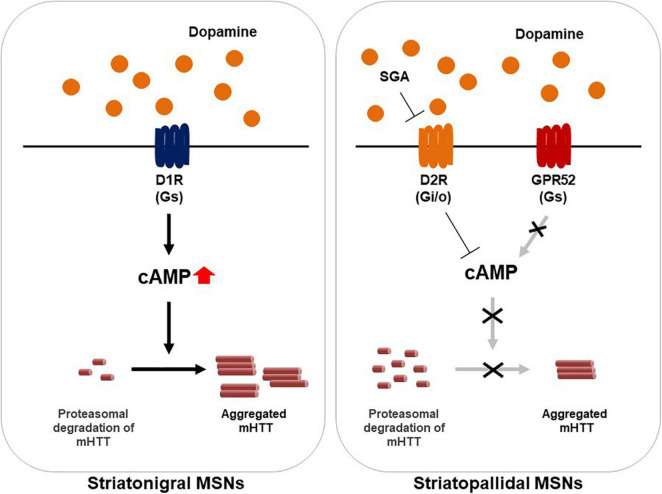
FIGURE 1.
A model illustrating of GPR52 inhibition for the treatment of Huntington’s disease. In the striatum, GPR52 is expressed in the striatopallidal MSNs in which dopamine D2 receptor (D2R) is expressed. GPR52 inhibition or the antagonists leads to proteasomal degradation of the mutant huntingtin protein (mHTT). Oppositely, GPR52 activation via intracellular cAMP rise transports mHTT to the endoplasmic reticulum and protects against its degradation. Meanwhile, GPR52 is not expressed in the striatonigral MSNs where dopamine D1 receptor (D1R) is expressed. Second generation antipsychotics (SGA), such as quetiapine, blocks D2R-mediated signaling.