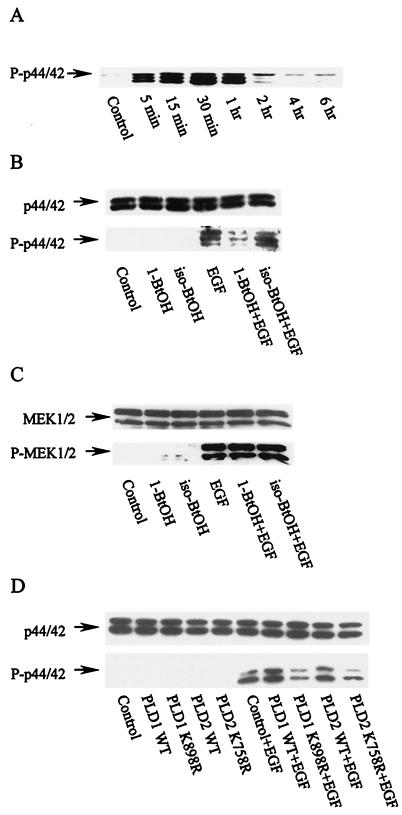
FIG. 8.
EGF-induced MAP kinase activation is dependent upon PLD. (A) The EGFR cells were treated with EGF (100 ng/ml). The cells were harvested at the time indicated and subjected to Western blot analysis using an antibody raised against phosphorylated MAP kinase (P-p42/44). (B) The EGFR cells were treated with EGF (100 ng/ml), where indicated, for 30 min in the absence or presence of the indicated alcohols (1%), which were added 5 min prior to EGF treatment. The cells were then harvested and subjected to Western blot analysis using either anti-MAP kinase (p44/42) antibody (upper panel) or anti-phosphorylated MAP kinase (P-p44/42) antibody (lower panel). (C) The samples shown in panel B were also analyzed for MEK1/2 and phosphorylated MEK1/2 by Western blot analysis using antibodies raised against either MEK1/2 (upper panel) or phosphorylated MEK1/2 (lower panel). (D) EGFR cells were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding either wild-type (WT) hPLD1 or mPLD2 or their catalytically inactive mutants hPLD1-K898R and mPLD2-K758R. The effect of EGF on the level of MAP kinase and phosphorylated MAP kinase was examined as for panel B. The data presented are representative results of an experiment that was repeated at least 2 times.